Ascariasis
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides. It is the most common form of soil-transmitted helminthiasis, affecting around 0.8 to 1.2 billion people globally, primarily in sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, and Asia.
Infection is often asymptomatic, particularly in cases with a low worm burden. However, symptomatic cases may present with respiratory and gastrointestinal symptoms. The disease is transmitted through ingestion of Ascaris eggs from contaminated food, water, or soil.

Signs and Symptoms
In populations with widespread worm infections, most people are infected by a small number of worms and usually have no symptoms. However, a small number of people may be heavily infected and symptomatic.
Migrating Larvae
Larval stages travelling through the body can cause visceral damage, peritonitis, liver or spleen enlargement, and lung inflammation. Pulmonary manifestations may present as Loeffler's syndrome, a transient respiratory illness associated with blood eosinophilia and pulmonary infiltrates.
Intestinal Blockage
In severe cases, worms can cause intestinal blockage, as seen in the X-ray of a South African patient. This may require surgical intervention. In some cases, worms may cause torsion and gangrene of the ileum.

Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction may occur, with worms sometimes blocking the ampulla of Vater or entering the biliary tree, causing acute pancreatitis, cholangitis, or cholecystitis.
Allergies and Malnutrition
Ascariasis may result in allergies to shrimp and dust mites due to shared antigens. It can also cause malnutrition through malabsorption and anorexia.
Other Symptoms
Ascaris worms may exit the body through the mouth when an infected person is under general anaesthesia.
Cause
Infection occurs through ingestion of Ascaris eggs from contaminated food, water, or soil. The eggs hatch in the intestines, and larvae migrate through the body, eventually reaching the lungs and then returning to the intestines to mature into adult worms.




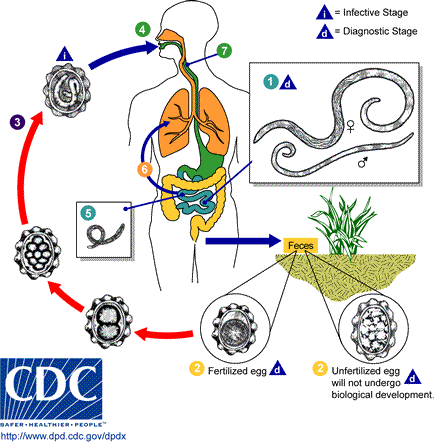
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically made by identifying Ascaris eggs or worms in faeces. The eggs have a characteristic oval shape with a thick, mamillated shell and can be seen under a microscope. During pulmonary disease, larvae may be found in fluids aspirated from the lungs. Radiographic imaging may show long filling defects or a whirled appearance of a bolus of worms.
Prevention
Prevention involves improved sanitation, including the use of clean toilets and proper disposal of faeces. Handwashing with soap is also protective. In areas where more than 20% of the population is affected, mass drug administration (MDA) is recommended, typically involving medications such as albendazole or mebendazole.
Treatment
Medications
Ascaricides recommended by the World Health Organisation include albendazole, mebendazole, levamisole, and pyrantel pamoate. These medications are effective in removing parasites and eggs from the intestines. Other effective agents include tribendimidine and nitazoxanide.
Surgery
In severe cases with bowel obstruction, emergency surgery may be required to manually remove the worms.
Epidemiology
Ascariasis is common in tropical and subtropical regions and is rare in developed or urban areas. The disease causes about 2,700 deaths annually, primarily among children in affected regions.


Research and Other Animals
Animal models, including mice and pigs, are used to study Ascaris infection. Ascariasis also affects pigs (Ascaris suum) and horses (Parascaris equorum), causing poor weight gain and financial losses for farmers.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the causative agent of Ascariasis?
In which regions is Ascariasis most commonly found?
What is the primary mode of transmission for Ascariasis?
Which of the following symptoms is associated with migrating larvae of Ascaris lumbricoides?
What complication may arise from a severe case of Ascariasis?
Which syndrome is associated with the pulmonary manifestations of Ascariasis?
How is Ascariasis typically diagnosed?
What is a recommended medication for treating Ascariasis according to the World Health Organisation?
In what scenario might surgery be required for a patient with Ascariasis?
Which of the following is a preventive measure for Ascariasis?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


