Breast Cancer
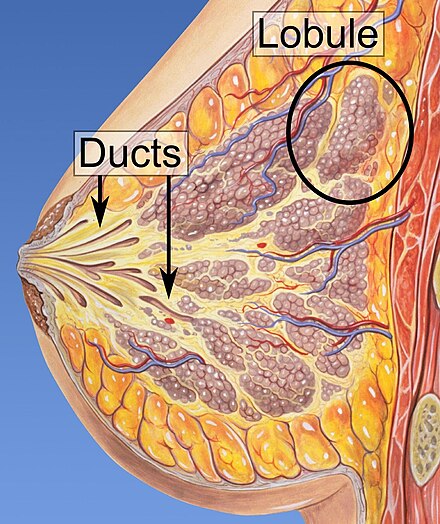
Breast cancer originates in mammary glands and is a significant concern in oncology. It is characterised by the development of malignant cells within the breast tissue, often detectable by screening or physical examination.
Signs and Symptoms
Most individuals with breast cancer are asymptomatic at diagnosis, detected through screening. When symptoms are present, they often include a new lump in the breast, swelling, pain, dimpling, redness, or dryness of the skin, and unusual nipple discharge. Less common forms, such as inflammatory breast cancer, cause significant swelling and redness, while Paget's disease presents with eczema-like changes around the nipple and areola.

Advanced breast cancer can metastasize, affecting bones, liver, lungs, and brain, leading to symptoms like bone pain, fractures, abdominal pain, jaundice, chest pain, cough, persistent headaches, seizures, and cognitive disruptions.
Screening
Mammography is the primary screening tool, involving low-dose X-ray imaging of the breast. It aids in detecting dense tissues, distortions, and microcalcifications. For dense breasts, other modalities like ultrasound, MRI, or tomosynthesis are preferred.

Regular screening significantly reduces breast cancer mortality. Medical guidelines recommend annual screening for women aged 50-70 years.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves imaging followed by a biopsy. Core needle biopsy is common, while fine-needle aspiration is used for fluid-filled masses. Post biopsy, breast cancers are classified by tissue origin, tumour grade, and receptor status (ER, PR, HER2).

Tumours are staged using the TNM system, incorporating tumour size (T), lymph node involvement (N), and metastasis (M).
Treatment
Local Tumours
Surgery is the primary treatment for localised tumours, ranging from lumpectomy to mastectomy. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is often performed to assess spread. Post-surgery, radiotherapy reduces recurrence risk. External beam radiotherapy is standard, though brachytherapy is an option.
Chemotherapy is used to lower recurrence risk, with drugs selected based on patient health and side effects profile. HER2-positive tumours benefit from trastuzumab, and hormone receptor-positive cancers are treated with endocrine therapies like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors.
Metastatic Disease
Metastatic breast cancer is managed with chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, HER2-targeted therapy, and other targeted treatments based on specific genetic mutations. Bone metastases are treated with bone-strengthening agents.
Supportive Care
Supportive care addresses side effects of treatment. Antiemetics manage nausea from chemotherapy, while antidepressants can alleviate hot flashes from endocrine therapy. Cognitive behavioural therapy, physical activity, and other interventions improve quality of life.

Risk Factors
Risk factors for breast cancer include hormonal influences, lifestyle choices, genetic predispositions, and certain medical conditions. Early menstruation, late menopause, late or no childbirth, and hormone replacement therapy increase risk. Lifestyle factors like alcohol consumption, obesity, and smoking also contribute. Genetic mutations, particularly in BRCA1 and BRCA2, significantly elevate risk.
Pathophysiology
Breast cancer arises from genetic mutations influenced by hormonal and environmental factors. Oestrogen promotes breast cell proliferation, and mutations in genes like PTEN and BRCA1/2 disrupt normal cell death pathways, leading to malignancy.
Prevention
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, breastfeeding, and, for high-risk individuals, preventive mastectomy or medications like SERMs and aromatase inhibitors.
Epidemiology
Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women, with incidence rising annually. It predominantly affects women over 50, though younger women and men can also develop the disease.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of breast cancer?
What is the primary screening tool for breast cancer?
Which of the following breast cancer types is known for significant swelling and redness?
What is the preferred biopsy method for diagnosing breast cancer?
Which hormone receptor status is considered in breast cancer classification?
Which drug is used specifically for HER2-positive breast cancer?
Which of the following factors does NOT increase the risk of breast cancer?
Which system is used to stage breast cancer?
For women aged 50-70 years, how often is regular screening for breast cancer recommended?
Which of the following is a preventive measure for high-risk individuals to reduce breast cancer risk?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


