Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition characterised by the compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel in the wrist.
This compression leads to a collection of symptoms and signs, most notably numbness and tingling in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the thumb side of the ring finger. The main cause of CTS is idiopathic, but other conditions like wrist fractures and rheumatoid arthritis can also lead to its development.

Anatomy

The carpal tunnel is an anatomical compartment located at the base of the palm. It contains nine flexor tendons and the median nerve. The median nerve provides sensation to the thumb, index finger, long finger, and half of the ring finger, as well as motor innervation to the muscles at the base of the thumb that allow it to abduct.
Pathophysiology
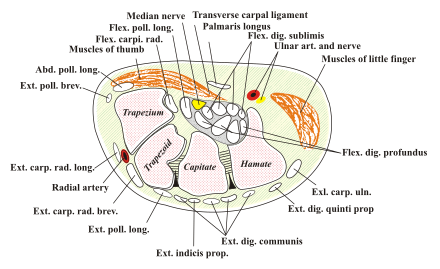
The median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel, which is formed by the carpal bones and the transverse carpal ligament. Increased pressure within this compartment can squeeze the median nerve, leading to decreased intraneural blood flow and subsequent nerve dysfunction. This process can result in demyelination and, in severe cases, axon injury.
Epidemiology
CTS is the most common nerve compression syndrome, affecting approximately 5-10% of the population. The condition is largely influenced by genetic factors, although other factors such as work-related tasks involving vibration, wrist extension or flexion, hand force, and repetition also play a role.
Signs and Symptoms
The characteristic symptoms of CTS include numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the thumb, index, middle, and radial half of the ring finger. Symptoms are typically worse at night, and patients often report awakening due to discomfort. In severe cases, there may be atrophy of the muscles at the base of the thumb and loss of sensibility.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on characteristic symptoms and physical examination findings. Electrodiagnostic tests, such as electromyography and nerve conduction velocity studies, can objectively measure and verify median neuropathy.
Provocative Tests
- Phalen's Manoeuvre: Fully flexing the wrist and holding the position to elicit symptoms.
- Tinel's Sign: Lightly tapping the median nerve to provoke paresthesia.
- Durkan Test: Applying firm pressure to the palm over the nerve.
- Hand Elevation Test: Lifting both hands above the head to provoke symptoms.
Treatment
Splint Immobilisation


Wrist splints alleviate symptoms by keeping the wrist straight, thus avoiding increased pressure in the carpal tunnel. They are primarily used at night.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroid injections may provide temporary symptom relief. However, they do not alter the disease's natural progression and are generally used as a short-term measure until more definitive treatments can be implemented.
Surgery

Surgical release of the transverse carpal ligament is the only treatment known to modify the disease course. It is recommended for cases with static numbness, muscle weakness, or atrophy.
Physical and Occupational Therapy
Manual therapy techniques, including soft tissue mobilisation, neurodynamic techniques, and carpal bone mobilisations, have shown efficacy in reducing pain and improving function in patients with CTS.
Prognosis

The natural history of untreated CTS is a gradual worsening of neuropathy. Advanced cases may result in permanent muscle atrophy and loss of sensibility. Surgical intervention can relieve symptoms but may not completely restore function if nerve damage is severe.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What nerve is compressed in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)?
Which of the following is NOT a typical symptom of CTS?
What anatomical structure forms the roof of the carpal tunnel?
Which test involves fully flexing the wrist to elicit symptoms of CTS?
What is the primary purpose of using a wrist splint in the treatment of CTS?
Which of the following is a definitive treatment for modifying the disease course of CTS?
What percentage of the population is affected by Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Which symptom is most commonly reported by patients with CTS during the night?
What type of therapy includes techniques like soft tissue mobilisation and neurodynamic techniques for CTS?
In severe cases of CTS, what kind of muscle damage can occur?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


