Chickenpox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable disease caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. The disease presents a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the chest, back, and face before spreading to the rest of the body. Other symptoms include fever, tiredness, and headaches.

Signs and Symptoms
The early symptoms in adolescents and adults include nausea, loss of appetite, aching muscles, and headache. This is followed by the characteristic rash or oral sores, malaise, and a low-grade fever. In children, the illness is not usually preceded by these prodromal symptoms, and the first sign is often the rash or oral spots. The rash starts as small red dots on the face, scalp, torso, upper arms, and legs, progressing over 10–12 hours to small bumps, blisters, and pustules, followed by scabbing.
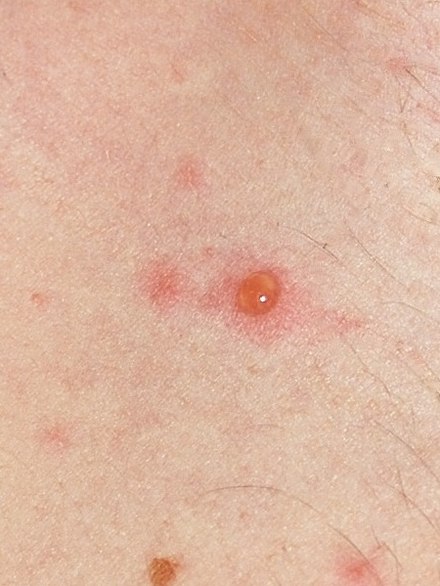
Blisters may also appear on the palms, soles, and genital area. The rash typically appears 10 to 21 days after exposure and usually resolves within a week or two. Adults often experience a more widespread rash and longer fever and are more likely to suffer complications, such as varicella pneumonia.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of chickenpox is primarily based on the clinical signs and symptoms, particularly the characteristic rash. Confirmation can be obtained by examining the fluid within the vesicles or by testing blood for immunologic response. Vesicular fluid can be examined using a Tzanck smear, direct fluorescent antibody testing, or viral culture. Blood tests can identify an acute infection (IgM) or previous infection and immunity (IgG).
Prevention
Hygiene Measures
The spread of chickenpox can be minimised by isolating affected individuals. The virus is susceptible to disinfectants like chlorine bleach and is sensitive to drying, heat, and detergents.
Vaccine
Chickenpox can be prevented by vaccination, which is part of the routine immunisation schedule in many countries, including the US. The varicella vaccine, developed in the 1970s, has significantly reduced the number of cases and complications. A second dose is recommended five years after the initial immunisation. The UK has not universally adopted the vaccine but recommends it for individuals particularly vulnerable to chickenpox.
Treatment
Treatment primarily focuses on symptom relief. Affected individuals are advised to stay home to avoid spreading the virus. Calamine lotion can help reduce itching, and maintaining good hygiene can prevent secondary bacterial infections. Paracetamol is recommended for fever reduction, but aspirin should be avoided due to the risk of Reye syndrome. For those at high risk of complications, antiviral medications like aciclovir may be prescribed.
Children
In children, the focus is on alleviating symptoms while the immune system manages the virus. Fingernails should be kept short to reduce scratching and secondary infections. Antivirals are not typically recommended for healthy children.
Adults
Infection is more severe in adults, so antiviral treatment is advised within 24–48 hours of rash onset. Adults should also stay hydrated and use painkillers like paracetamol to relieve symptoms. Antihistamines might be used to manage severe itching and to aid sleep.
Prognosis
The visible blistering usually resolves within four to seven days in children. Adults experience more severe symptoms and complications, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, hepatitis, and encephalitis. Pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals are at a higher risk of severe disease. Secondary bacterial infections are the most common complication in healthy children.


Epidemiology
Chickenpox is prevalent worldwide, with an infection rate of 90% in close contacts. In temperate countries, it is primarily a childhood disease, while in tropical regions, it often occurs in older individuals and is more severe. The introduction of the varicella vaccine in the US has led to a significant reduction in cases and complications.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Sure! Here are the formatted questions in HTML and pseudocode:
What is chickenpox caused by?
Which of the following is NOT a typical symptom of chickenpox in children?
What is the typical duration for the chickenpox rash to resolve?
Which of the following treatments is NOT recommended for chickenpox?
Which diagnostic test can confirm a chickenpox infection by examining vesicular fluid?
Which age group is more likely to suffer complications from chickenpox?
Which of the following measures can help prevent the spread of chickenpox?
What is the primary focus of treatment for chickenpox?
What is the recommended action for managing fever in chickenpox patients?
How has the varicella vaccine impacted the incidence of chickenpox?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


