Dermatophytosis
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea or ringworm, is a fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. It manifests as a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash and can lead to hair loss in the affected area. Symptoms typically begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are named based on the body area they affect, and multiple areas can be simultaneously infected.

Types
There are about 40 types of fungi that can cause dermatophytosis, mainly from the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton. The disease patterns are identified by the area of the body they infect:
- Tinea pedis (athlete's foot): Fungal infection of the feet.
- Tinea unguium: Fungal infection of the fingernails, toenails, and the nail bed.
- Tinea corporis: Fungal infection of the arms, legs, and trunk.
- Tinea cruris (jock itch): Fungal infection of the groin area.
- Tinea manuum: Fungal infection of the hands and palm area.
- Tinea capitis: Fungal infection of the scalp and hair.
- Tinea faciei: Fungal infection of the face.
- Tinea barbae: Fungal infestation of facial hair.
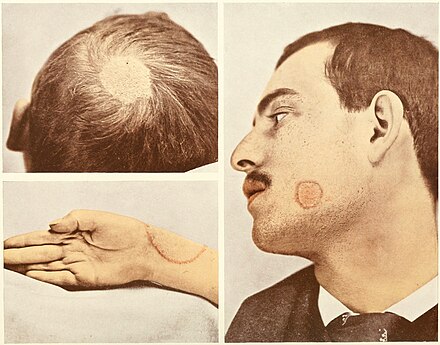
Certain conditions that are not classic ringworm, such as tinea versicolor and tinea nigra, are also caused by fungi but not dermatophytes.
Signs and Symptoms
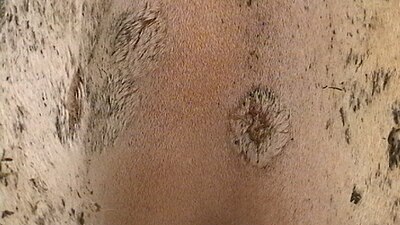
Dermatophytosis typically presents with red, scaly, itchy, or raised patches that might be redder on the outside edges or resemble a ring. These patches can ooze or develop blisters, and bald patches may develop if the scalp is affected. In the feet, it causes athlete's foot; in the groin, it results in jock itch; and in nails, it leads to onychomycosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Fungi thrive in moist, warm areas such as locker rooms, tanning beds, swimming pools, and skin folds. They spread through direct contact with infected individuals or animals, or by sharing contaminated items like towels, clothing, or hairbrushes. Risk factors include using public showers, engaging in contact sports, excessive sweating, obesity, and poor immune function.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of dermatophyte infections is based on clinical history, physical examination, and potassium hydroxide (KOH) microscopy.
Prevention
Preventive measures include avoiding sharing personal items, washing clothes in hot water with fungicidal soap after suspected exposure, wearing protective shoes in public places, and avoiding touching pets with bald spots.
Treatment
Antifungal treatments are effective against dermatophytosis. Topical agents like miconazole, terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, or tolnaftate are applied twice daily until symptoms resolve, typically within one or two weeks. Treatment should continue for seven days after visible symptoms disappear to prevent recurrence. Severe cases or scalp ringworm may require systemic treatment with oral medications such as itraconazole, terbinafine, and ketoconazole. Good hygiene and avoiding touching lesions are very important to prevent spreading the infection.
History
Described since ancient times, dermatophytosis was treated with mercury, sulphur, or iodine compounds before 1906. Hairy areas, particularly the scalp, were treated with X-rays followed by antifungal medication.
Terminology
The term "ringworm" is a misnomer because the infection is caused by fungi, not by parasitic worms.
Dermatophytosis in Animals
Ringworm affects various animals and can be transmitted between animals and humans. In cattle, lesions are typically found on the head, neck, tail, and perineum. Treatment in animals involves systemic oral treatment and topical "dip" therapies.





Epidemiology
Dermatophytosis affects up to 20-25% of the global population, with varying prevalence based on geographic location and population demographics. Infections are more common in tropical regions and in certain age groups, such as children for scalp infections and the elderly for groin infections.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which of the following is NOT a type of dermatophytosis?
What is the primary cause of dermatophytosis?
Which of the following is a common symptom of dermatophytosis?
What is the typical incubation period for dermatophytosis symptoms to appear after exposure?
Which of the following is a risk factor for developing dermatophytosis?
Which diagnostic method is commonly used to identify dermatophyte infections?
What is the recommended treatment duration with topical antifungal agents after symptoms of dermatophytosis disappear?
Which of the following is NOT a genera of fungi that cause dermatophytosis?
Which type of tinea affects the scalp and hair?
Which of the following measures can help prevent dermatophytosis?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


