Down Syndrome
Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. This disorder is usually associated with developmental delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic physical features.
The most common type is trisomy 21, accounting for the majority of cases, followed by mosaic (2%) and translocation (3%) Down syndrome.
Signs and Symptoms
People with Down syndrome typically have physical and intellectual disabilities. Their mental abilities are often similar to those of an 8- or 9-year-old, but their emotional and social awareness can be high. They are prone to various health issues, including congenital heart defects, epilepsy, leukaemia, and thyroid diseases.

Physical Characteristics
Common physical traits include a small chin, epicanthic folds, low muscle tone, a flat nasal bridge, a single crease of the palm, and a protruding tongue. Other features can include excessive joint flexibility, extra space between the big toe and second toe, and short fingers. Atlantoaxial instability, a condition affecting the cervical spine, occurs in about 1–2% of cases.

Neurological
Down syndrome often causes intellectual disability, with most individuals having mild to moderate impairment. Developmental milestones are delayed, with walking typically occurring around 1-4 years. Commonly, individuals have better language understanding than speaking abilities. Behavioural issues are generally less severe than in other intellectual disabilities, although mental illness is prevalent in nearly 30% of cases.
Senses
Hearing and vision disorders occur in more than half of people with Down syndrome.

Diagnosis
Screening Before Birth
Prenatal screening is recommended for all pregnant women. Ultrasound can show markers like increased nuchal translucency, while blood tests measure markers like α-fetoprotein and hCG. If screening indicates a high likelihood, diagnostic tests like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling confirm the diagnosis.
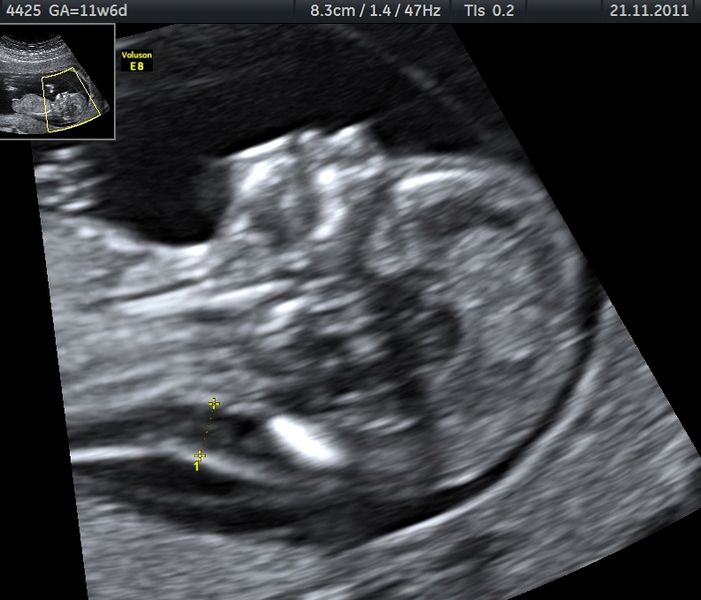
After Birth
Diagnosis can often be made based on physical appearance at birth, confirmed by chromosomal analysis to identify the presence of an extra chromosome 21.
Treatment
There is no cure for Down syndrome, but treatment focuses on improving quality of life. This includes physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Education and support in a work environment are also beneficial.
Health Screening
Regular health checks are recommended to monitor for common issues. These include:
- Hearing: Six months, 12 months, then yearly.
- Eyes: Six months, then yearly.
- Teeth: Two years, then every six months.
- Celiac Disease: Between 2-3 years of age or earlier if symptoms occur.
- Sleep Study: Three to four years or earlier if symptoms of obstructive sleep apnoea occur.
- Neck X-rays: Between three and five years of age.
Cognitive Development
Interventions may include hearing aids for hearing loss, speech therapy, and learning sign language or alternative communication methods. Education programmes and inclusive schooling can help develop cognitive skills, while physical therapy aids motor development.
Other Treatments
Tympanostomy tubes may be needed multiple times during childhood for ear infections, and tonsillectomy can help with sleep apnoea and throat infections. In cases of dementia, medications like memantine, donepezil, rivastigmine, or galantamine may be used.
Prognosis
With improved medical care, life expectancy for individuals with Down syndrome has increased significantly. While the average lifespan is around 50-60 years in the developed world, some individuals live into their 70s. Most adults with Down syndrome require assistance with financial, medical, and legal matters, but many can live semi-independently and engage in paid work.
Epidemiology
Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal abnormality, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 births globally. Maternal age is a significant risk factor, with chances increasing with age. However, 70% of children with Down syndrome are born to women 35 years of age or younger, as younger women tend to have more children.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the most common type of Down syndrome?
Which of the following physical characteristics is NOT commonly associated with Down syndrome?
What percentage of people with Down syndrome have mosaic Down syndrome?
Which of the following is a common neurological feature of Down syndrome?
Which diagnostic test is used to confirm Down syndrome before birth if screening indicates a high likelihood?
At what age is a sleep study recommended for individuals with Down syndrome?
Which of the following health checks is NOT recommended yearly for individuals with Down syndrome?
What is the average life expectancy for individuals with Down syndrome in the developed world?
What percentage of children with Down syndrome are born to women 35 years of age or younger?
Which of the following is NOT a treatment focus for individuals with Down syndrome?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


