Folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles, which can occur on any hair-covered skin. It manifests as pimples that develop white tips and can appear on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head. While acne may involve superficial infection and inflammation of some hair follicles, folliculitis is distinguished as a separate condition primarily caused by factors other than acne.

Signs and Symptoms

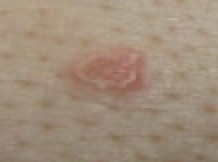
Folliculitis presents with various signs and symptoms, including:
- A rash characterised by reddened skin areas.
- Itching skin.
- Pimples or pustules located around a hair or follicle, which can crust over and are typically found on the neck, armpit, or groin. These lesions can sometimes be mistaken for chicken pox and may present as genital lesions.
- Mismanaged antibiotic treatment can lead to the spreading of the condition from one area of the body to another, such as from the leg to the arm.
Complications
Folliculitis can escalate into severe skin conditions like cellulitis or abscess if not properly managed.
Causes
Most cases of folliculitis, including carbuncles and boils, are infected with Staphylococcus aureus. The condition begins with the introduction of a pathogen to a hair follicle which can be damaged by friction from clothing, insect bites, follicle blockage, shaving, or tight braids. Damaged follicles become susceptible to infection by Staphylococcus spp. Chronic cases of folliculitis can sometimes be associated with iron-deficiency anaemia.
Bacterial Causes
- Staphylococcus aureus folliculitis.
- Hot-tub folliculitis, caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, typically occurs after using a poorly cleaned hot tub.
- Sycosis vulgaris (barber's itch) is a staphylococcal infection of facial hair follicles, aggravated by shaving.
- Gram-negative folliculitis may emerge after prolonged acne antibiotic treatment.
Fungal Causes
- Tinea barbae is a fungus-caused condition similar to barber's itch.
- Malassezia folliculitis is caused by yeasts of the genus Malassezia.
Mites
- Demodex folliculitis results from an overgrowth of Demodex folliculorum mites, particularly in individuals with oily scalps.
Viral Causes
- Herpetic folliculitis is a rare condition where herpes simplex virus infects nearby hair follicles, usually around the mouth.
Noninfectious Causes
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae occurs when hair curls back into the skin, causing inflammation.
- Eosinophilic folliculitis is seen in individuals with compromised immune systems.
- Folliculitis decalvans or tufted folliculitis affects the scalp, leading to scarring and permanent hair loss.
- Folliculitis keloidalis involves scarring on the nape of the neck, common in males with curly hair.
- Oil folliculitis results from exposure to oils, often affecting refinery workers, road workers, mechanics, and sheep shearers. Even makeup can cause it.
- Recalcitrant cases may indicate malignancy.
Treatment
Simple cases of folliculitis often resolve on their own. However, treatment usually involves topical medications:
- Topical antiseptic treatment is sufficient for most cases.
- Topical antibiotics such as mupirocin or neomycin/polymyxin B/bacitracin ointment may be prescribed, and oral antibiotics may be used.
- Systemic narrow-spectrum penicillinase-resistant penicillins (e.g., dicloxacillin in the US or flucloxacillin in the UK) may benefit some patients.
- Fungal folliculitis may require oral antifungals like fluconazole or topical antifungals such as econazole nitrate.
Folliculitis has a tendency to recur even after symptoms subside.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is folliculitis primarily characterised by?
Which pathogen is most commonly associated with folliculitis?
What is a potential complication of untreated folliculitis?
What type of folliculitis is associated with the use of poorly cleaned hot tubs?
What is the primary cause of barber’s itch?
What type of folliculitis might occur due to an overgrowth of mites?
Which population is most likely to experience eosinophilic folliculitis?
What treatment is often sufficient for most simple cases of folliculitis?
Which of the following is a noninfectious cause of folliculitis?
Which condition involves scarring and permanent hair loss on the scalp due to folliculitis?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


