Foodborne illness
Foodborne illness (also known as foodborne disease or food poisoning) encompasses any illness resulting from the contamination of food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites, prions, and toxins such as aflatoxins in peanuts, poisonous mushrooms, and various beans that have not been boiled for at least 10 minutes.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of foodborne illness vary depending on the contaminant but often include vomiting, fever, and aches, with potential diarrhoea. Vomiting can be repeated with delays in between, as microbes may pass through the stomach into the intestine and multiply. Incubation periods vary, leading to delays in symptom onset from hours to days, which can obscure the connection to the contaminated food.

Causes
Foodborne illness usually arises from improper handling, preparation, or storage of food. Good hygiene practices are very important in reducing the chances of contracting an illness. Regular hand-washing is an effective defence against spreading foodborne pathogens. Foodborne illness can also be caused by chemicals like pesticides, medicines, and natural toxic substances.
Bacteria
Bacteria are a common cause of foodborne illness. Common bacterial pathogens include Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella, and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Bacterial toxins require time to multiply, causing symptoms to appear 12–72 hours after ingestion.
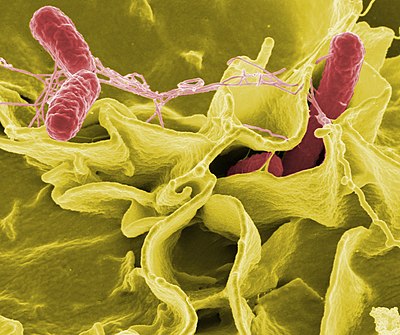
Enterotoxins, exotoxins targeting the intestines, can produce illness even when the microbes have been killed. For example, Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins can cause symptoms within one to six hours.
Emerging Pathogens
Emerging pathogens like Aeromonas hydrophila and Yersinia enterocolitica are being increasingly linked to outbreaks, often from contaminated pre-washed salads.

Viruses
Viral infections are responsible for about one-third of food poisoning cases in developed countries, with noroviruses being the most common. Viral infections usually have an incubation period of 1–3 days and are self-limited in healthy individuals.

Parasites
Foodborne parasites are usually zoonoses, meaning they are transmitted from animals to humans. Common parasites include Anisakis, Giardia lamblia, and Toxoplasma.
Natural Toxins
Plants and some animals naturally contain toxins. Examples include solanine in green potatoes and tetrodotoxin in fugu fish. Some plants contain toxic substances that have therapeutic properties in appropriate dosages.
Other Pathogenic Agents
Prions, responsible for diseases like Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), can also cause foodborne illnesses.
Mechanism
Incubation Period
The incubation period, or the delay between food consumption and the appearance of symptoms, ranges from hours to days. The length of the incubation period can influence the type of illness and its diagnosis.
Infectious Dose
The infectious dose is the amount of pathogen that must be ingested to cause illness. This varies with the type of pathogen and the health status of the consumer. For example, Shigella sonnei has a low infectious dose, while Staphylococcus aureus has a higher infectious dose.
Epidemiology
Infants
Infants are particularly vulnerable to foodborne diseases. The World Health Organisation recommends breastfeeding to protect infants from foodborne infections.
United States
A CDC report from 2017–2019 found that 41% of restaurant outbreaks were caused by sick employees. Common causes of foodborne illness include norovirus, Salmonella, and Clostridium perfringens.
United Kingdom
The Food Standards Agency reported around a million cases of foodborne illness per year, resulting in 20,000 hospitalizations and 500 deaths.
Australia
A 2022 study estimated 4.67 million cases of food poisoning in Australia annually, causing 47,900 hospitalizations and 38 deaths.
Outbreaks
Outbreaks occur when two or more people experience similar illness after consuming food from a common source. Outbreaks can be identified through public health surveillance and laboratory results.
Society and Culture
United Kingdom
Several serious outbreaks, such as the 1964 typhoid contamination in Aberdeen and the 1996 Wishaw E. coli O157 outbreak, have led to significant changes in UK food safety laws.
United States
Foodborne illness remains a significant concern, with ongoing efforts to improve food safety regulations and public awareness.
Organisations
The World Health Organisation and the International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN) work globally to prevent the spread of contaminated food and foodborne diseases.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is foodborne illness also known as?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of foodborne illness?
Which bacterium is commonly associated with foodborne illness?
What is the most common viral cause of foodborne illness in developed countries?
Which of the following is a foodborne parasite?
What is the incubation period in the context of foodborne illness?
Which natural toxin is found in green potatoes?
Which pathogen is known for having a very low infectious dose?
According to the CDC report from 2017–2019, what percentage of restaurant outbreaks were caused by sick employees?
Which international organisation works globally to prevent the spread of contaminated food and foodborne diseases?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


