Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood effectively to meet the body's needs. This results in symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swollen legs. HF can be caused by various conditions, including heart attacks, high blood pressure, and infections.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of heart failure are often categorized based on which side of the heart is affected. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and swelling of the legs.
Left-Sided Heart Failure
The left side of the heart pumps oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the rest of the body. Failure here leads to blood backing up into the lungs, causing respiratory symptoms like increased respiratory rate, laboured breathing, and pulmonary oedema. Other signs include a displaced apex beat and a gallop rhythm. Patients may also experience orthopnea (difficulty breathing while lying down) and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (sudden nighttime shortness of breath).
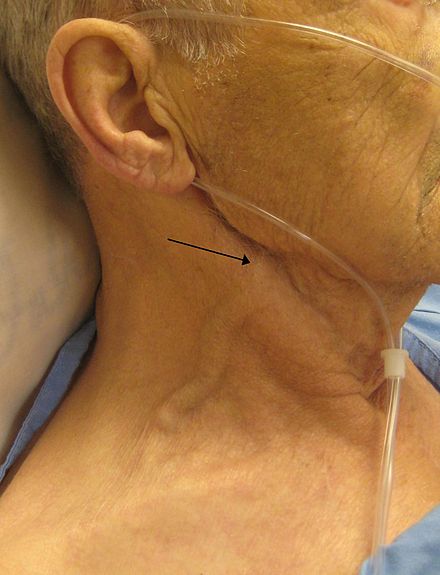
Right-Sided Heart Failure
Right-sided heart failure, often caused by pulmonary hypertension or pulmonic stenosis, results in fluid accumulation in the body's tissues, leading to peripheral oedema, ascites, and liver enlargement. Jugular venous pressure is often elevated.
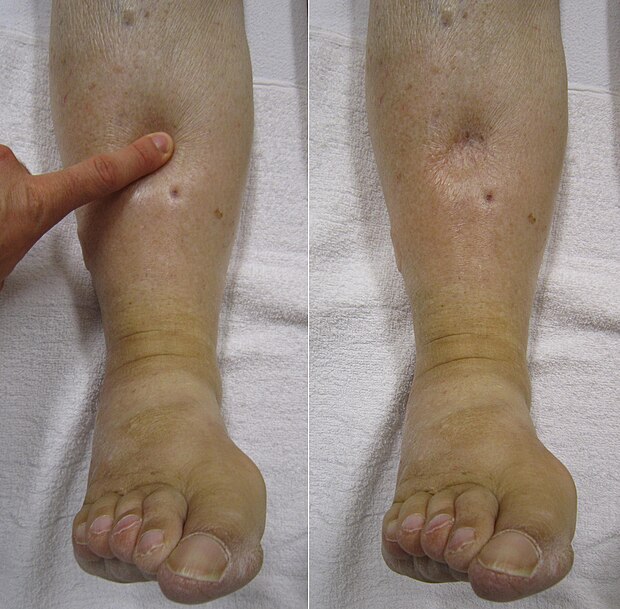
Biventricular Failure
In biventricular failure, both sides of the heart are affected, leading to symptoms of both left and right heart failure, including pleural effusion.

Causes
Heart failure can result from various conditions that alter the heart's structure or function. Common causes include:
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- High blood pressure
- Atrial fibrillation
- Valvular heart disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Cardiomyopathy
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves assessing symptoms, physical findings, and using diagnostic tools such as echocardiography, blood tests, and chest X-rays.
Echocardiography
An echocardiogram is commonly used to evaluate heart function, determine ejection fraction, and identify structural abnormalities.
Chest X-ray
Chest X-rays can show cardiomegaly and signs of pulmonary oedema, such as Kerley B lines.

Blood Tests
N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels are biomarkers used to diagnose heart failure.
Treatment
Treatment focuses on improving symptoms and preventing disease progression. Management strategies include lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes device therapy or surgery.
Lifestyle Changes
Patients are advised to stop smoking, engage in physical exercise, and follow a heart-healthy diet. Fluid and salt intake may need to be restricted.
Medications
First-line medications include:
- Diuretics: To reduce fluid retention.
- ACE inhibitors/ARBs: To lower blood pressure and decrease heart workload.
- Beta blockers: To slow heart rate and reduce blood pressure.
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: For further blood pressure control.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: For patients with reduced ejection fraction.
Devices and Surgery
In severe cases, implanted devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardiac defibrillators may be recommended. In advanced heart failure, ventricular assist devices or heart transplantation may be necessary.
Palliative Care
For end-stage heart failure, palliative care focuses on symptom management and quality of life.
Heart failure is a complex condition requiring comprehensive management to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical for managing symptoms and slowing disease progression.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which of the following is the most common cause of right-sided heart failure?
What is a common symptom of left-sided heart failure?
Which diagnostic tool is most commonly used to assess ejection fraction in heart failure patients?
What is the primary goal in the acute management of decompensated heart failure?
Which medication is recommended for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and has shown to improve survival?
Which condition is NOT commonly associated with causing heart failure?
What is the most likely physical finding in a patient with right-sided heart failure?
Which of the following is a non-pharmacological treatment recommended for managing chronic heart failure?
In which patient population is heart failure most commonly seen?
What is a characteristic feature of high-output heart failure?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!