Hodgkin lymphoma
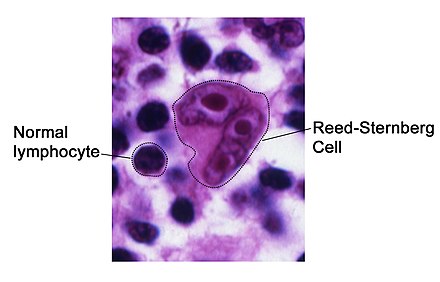
Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL) is a type of blood and immune-system cancer that originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes. The condition was named after Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. HL is characterised by the presence of multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) in the lymph nodes.
Signs and Symptoms
People with Hodgkin lymphoma may present with the painless enlargement of one or more lymph nodes, typically in the neck, armpits, or groyne. These nodes may feel rubbery and swollen upon examination. Systemic symptoms, known as B symptoms, include itchy skin, night sweats, unexplained weight loss, low-grade fever, and fatigue. Enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly) and liver (hepatomegaly) can also occur. Rare but specific symptoms include pain following alcohol consumption and cyclical high-grade fever known as Pel–Ebstein fever.

Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Hodgkin lymphoma is confirmed through a lymph node biopsy, typically followed by microscopic examination to identify RS cells. Blood tests assess major organ function and chemotherapy safety, while imaging techniques such as PET scans are used to detect small deposits of cancer. PET scans also help in functional imaging by using radiolabeled glucose. In some cases, a gallium scan may be used instead.

Types
Hodgkin lymphoma is classified into two main types: classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL). Classic Hodgkin lymphoma can be further subdivided based on the morphology of RS cells and the composition of reactive cell infiltrate.
- Nodular sclerosing HL: The most common subtype, characterised by large tumour nodules and scattered RS cells within a background of lymphocytes and plasma cells with collagen fibrosis.
- Mixed-cellularity subtype: Composed of numerous RS cells and inflammatory cells, often associated with EBV infection.
- Lymphocyte-rich: Rare, with many features that may cause diagnostic confusion with NLPHL. It has a favourable prognosis.
- Lymphocyte-depleted: Contains large numbers of pleomorphic RS cells and fewer reactive lymphocytes, often confused with diffuse large cell lymphoma.

Staging
Staging of Hodgkin lymphoma follows the Ann Arbour staging classification, ranging from Stage I to Stage IV, based on lymph node involvement and the presence of systemic symptoms. PET scans are used to stage the disease accurately.




Pathology
Affected lymph nodes are typically enlarged but maintain their shape. Microscopic examination reveals complete or partial effacement of lymph node architecture by RS cells, surrounded by a reactive cell infiltrate. RS cells have specific characteristics, including large size, abundant cytoplasm, and the presence of "owl eyes" nuclei.

Treatment
Treatment options for Hodgkin lymphoma include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem-cell transplantation. Early-stage disease is often treated with either radiation therapy or chemotherapy, while later stages typically require combination chemotherapy. Common chemotherapy regimens include ABVD, MOPP, Stanford V, and BEACOPP.
Radiation therapy involves external beam radiation to affected lymph nodes and may be combined with chemotherapy. Long-term concerns include secondary malignancies and cardiovascular disease due to treatment.
Prognosis
The prognosis for Hodgkin lymphoma is generally favourable, especially with early detection and treatment. The five-year survival rate in the United States is approximately 88%, with even higher rates in younger populations. Prognosis is influenced by various factors, including age, stage of disease, and early response to treatment.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Who first described Hodgkin Lymphoma?
What type of cells are characteristic of Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Which imaging technique is commonly used to stage Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Which subtype of classic Hodgkin Lymphoma is the most common?
Which of the following is NOT a systemic B symptom of Hodgkin Lymphoma?
What is the five-year survival rate for Hodgkin Lymphoma in the United States?
What is the primary method for confirming a diagnosis of Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Which type of Hodgkin Lymphoma is often associated with EBV infection?
What is the distinctive appearance of Reed–Sternberg cells under a microscope?
Which chemotherapy regimen is commonly used to treat Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


