Hookworm Infection
Hookworm infection is a medical condition caused by intestinal parasites known as hookworms. The two primary species infecting humans are Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. Hookworm infection primarily affects individuals in warm climates with poor sanitation and is classified as a neglected tropical disease.
Signs and Symptoms
Hookworm infection can be asymptomatic, especially in individuals with a low worm burden. Early symptoms may include itching and a localised rash at the site of larval penetration, known as ground itch. As the infection progresses, gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, and indigestion may occur. Chronic, heavy infections can lead to severe iron-deficiency anaemia and protein deficiency, manifesting as fatigue, weakness, pallor, and in extreme cases, cardiac failure and oedema. In children, chronic infection can impair growth, intellectual, and cognitive development.
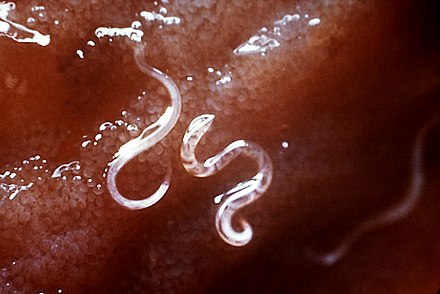
Cause
Human hookworm infections are caused by Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. Other animals, including dogs and cats, can also be infected by species such as A. caninum, A. tubaeforme, and A. braziliense. Humans typically acquire the infection through direct skin contact with contaminated soil containing infective larvae.

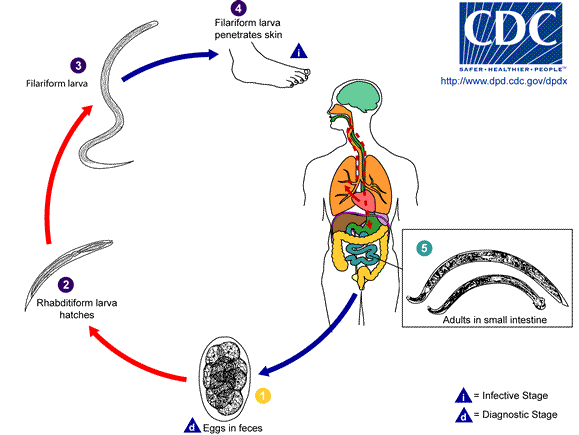
Life Cycle
Hookworms thrive in warm, moist soil. The larvae penetrate the skin, usually through the feet, travel via the bloodstream to the lungs, ascend the trachea, and are swallowed to reach the intestines, where they mature into adults. The adult worms attach to the intestinal walls, causing blood loss and laying thousands of eggs daily, perpetuating the cycle.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of hookworm infection is primarily based on the microscopic examination of stool samples to detect hookworm eggs. The eggs are oval, colourless, and have a thin transparent shell. Advanced diagnostic techniques, such as DNA-based tools, are being developed for more accurate identification.

Prevention
Preventive measures include avoiding walking barefoot in areas known to be contaminated, using proper sanitation facilities, and not using untreated human excreta as fertiliser. Deworming pets can also prevent zoonotic transmission. Public health education and mass deworming programmes, especially in schools, are very important in reducing infection rates.

Treatment
The treatment for hookworm infection includes the administration of anthelmintic drugs such as albendazole and mebendazole, which are effective against adult worms. Iron supplements may be required for individuals with anaemia. In cases where the infection is still in the skin, local cryotherapy can be used.
Epidemiology
Hookworm infections affect millions worldwide, with the highest prevalence in sub-Saharan Africa, East Asia, and the Pacific Islands. Many infected individuals live in poverty-stricken areas with inadequate sanitation, exacerbating the spread of the disease.

History
The hookworm's link to disease dates back to ancient Egypt, with modern identification by Angelo Dubini in 1838. Significant eradication efforts began in the early 20th century, notably with the Rockefeller Sanitary Commission's work in the southern United States, which significantly reduced infection rates through public education and improved sanitation.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which of the following species is a primary cause of hookworm infection in humans?
What is the initial symptom that may occur at the site of larval penetration in hookworm infection?
Hookworms primarily thrive in which type of environment?
How do humans typically acquire hookworm infections?
What is the primary method of diagnosing hookworm infection?
Which drug is commonly used to treat hookworm infection?
What severe condition can chronic, heavy hookworm infection lead to?
Which of the following is a preventive measure for hookworm infection?
In which regions is hookworm infection most prevalent?
When did significant eradication efforts for hookworm infection begin in the southern United States?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


