Huntington's disease

Signs and Symptoms
Initial symptoms often include subtle mood changes and cognitive decline. Physical symptoms typically follow, characterised by involuntary movements (chorea), lack of coordination, and an unsteady gait. As the disease progresses, symptoms worsen, leading to severe motor dysfunction, speech and swallowing difficulties, and dementia. Juvenile HD presents with symptoms resembling Parkinson's disease, such as slow movements and rigidity, often coupled with seizures.
Genetics
Huntington's disease is caused by a mutation in the huntingtin gene (HTT) on chromosome 4. The mutation involves an expansion of CAG trinucleotide repeats. Individuals with fewer than 36 repeats generally do not develop HD, while those with more than 40 repeats will be affected. The disease follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning a child has a 50% chance of inheriting the disorder if one parent is affected.
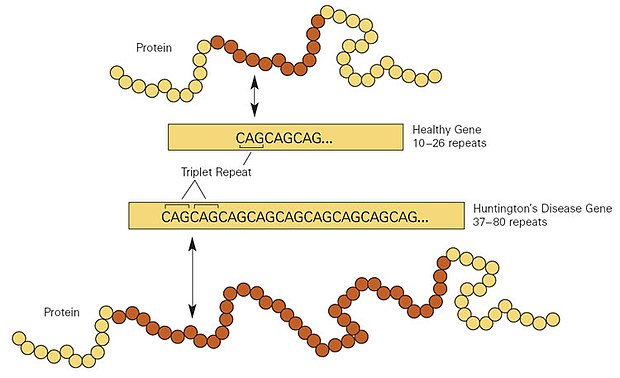
Mechanisms
The mutant huntingtin protein (mHtt) causes neurodegeneration, primarily affecting the basal ganglia and later the cerebral cortex. This results in the hallmark symptoms of HD. Other affected brain areas include the substantia nigra, hippocampus, and thalamus. The protein's toxicity manifests through multiple pathways, including mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired protein clearance, and transcriptional dysregulation.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with the observation of physical symptoms, supported by genetic testing to confirm the presence of the expanded CAG repeats in the HTT gene. Predictive genetic testing is available for at-risk individuals. Imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans can show brain atrophy, particularly in the caudate nuclei.

Treatment
There is no cure for HD, but treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Tetrabenazine is approved for treating chorea, while antipsychotics and benzodiazepines can help reduce other motor symptoms. Antidepressants and antipsychotic medications are used to manage psychiatric symptoms. Physical, occupational, and speech therapies are essential for maintaining function and quality of life. Nutritional support is also very important due to difficulties in swallowing and weight loss.

Prognosis
Life expectancy for individuals with HD is generally 10 to 30 years following symptom onset. Common causes of death include pneumonia, heart disease, and complications from falls or choking. Suicide is a significant risk, particularly in the mid-stages of the disease.
Epidemiology
HD prevalence varies globally, with the highest rates in individuals of Western European descent. In the UK, the average prevalence is 12.3 per 100,000. Some isolated populations, such as the Lake Maracaibo region in Venezuela, show much higher prevalence due to founder effects.
History
The first detailed description of HD was provided by George Huntington in 1872. The genetic basis of the disease was identified in 1993 through international collaboration led by the Hereditary Disease Foundation. This discovery has paved the way for extensive research into the mechanisms and potential treatments for HD.

Support Organisations
Numerous organisations support HD research and provide resources for affected individuals and their families. Key organisations include the Hereditary Disease Foundation and the Huntington's Disease Society of America.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary cause of Huntington's Disease (HD)?
Which brain area is most affected in the early stages of Huntington's Disease?
What type of inheritance pattern does Huntington's Disease follow?
Which medication is approved for treating chorea in Huntington's Disease?
What is the typical age range for the onset of Huntington's Disease symptoms?
Which of the following is a common cause of death in individuals with Huntington's Disease?
What is the primary symptom of juvenile Huntington's Disease that resembles Parkinson's Disease?
What does an MRI scan of a patient with Huntington's Disease typically show?
In which population is the prevalence of Huntington's Disease particularly high due to founder effects?
Who provided the first detailed description of Huntington's Disease?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


