Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a common congenital condition affecting the male reproductive system, where the urethral opening is not located at the tip of the penis but elsewhere along the underside. It is the second-most frequent birth defect in male genitalia, occurring in approximately one out of every 250 male births. The condition ranges in severity, with 90% being less severe (distal hypospadias) and the remaining 10% more severe (proximal hypospadias).

Signs and Symptoms
A penis affected by hypospadias typically presents with a characteristic appearance. The urinary opening (meatus) is positioned lower than usual, and the foreskin is often partially developed, giving the glans a hooded look. Chordee, or a downward curvature of the penis, can also occur, especially in more severe cases. In some instances, the foreskin appears typical, and the hypospadias is only discovered during circumcision or later in childhood.
Complications
Hypospadias can lead to complications, including erectile problems and difficulties with ejaculation, particularly when chordee is present. The condition can also interfere with urination, causing a spraying stream that may require sitting to urinate. Surgical intervention may be sought to correct these issues.
Cause
Genes and Prenatal Hormones
The exact cause of hypospadias remains unknown, though genetic and environmental factors are suspected. Sexual differentiation in foetuses involves prenatal sex hormones, and disruptions in this process can lead to hypospadias.
Epigenetic Inheritance Hypothesis
Identical twin studies and animal research have suggested a role for epigenetic markers in the development of hypospadias. These markers might affect androgen signalling and contribute to the condition. Recent studies have found atypical epigenetic methylation in hypospadias patients, but further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Diagnosis
Hypospadias is typically diagnosed at birth through physical examination. The presence of chordee, undescended testicles, or other genital abnormalities might prompt further testing to rule out intersex conditions or hormonal deficiencies. Routine blood tests or X-rays are not usually required unless other conditions are suspected.

Treatment
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is not always necessary for minor hypospadias. However, when intervention is required, surgical techniques can extend the urethra to the tip of the penis, straighten chordee, and adjust the foreskin. The most common surgical method is the Tubularized Incised Plate (TIP) repair, which is effective for distal hypospadias with a complication rate of less than 10%.
For proximal hypospadias, TIP repair is successful in about 85% of cases. Severe cases might require multiple surgeries, including the use of preputial or buccal mucosa grafts. Complications such as fistulas, diverticula, and strictures can arise, necessitating further surgical corrections.
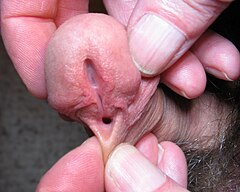

Age at Surgery
Surgical outcomes are generally consistent regardless of the patient's age, though most repairs are performed in childhood. Hormonal treatments, such as testosterone or hCG, might be used preoperatively to increase penile size and improve surgical success.
Postoperative Considerations
Postoperative complications are usually identified within six months but can sometimes emerge later. Common issues include fistulas, meatal stenosis, and glans dehiscence. Additional surgeries might be required for correction.
Epidemiology
Hypospadias is one of the most common birth defects worldwide, affecting up to 4% of newborn males in milder cases. Variations in reporting standards can complicate the accurate determination of its incidence.
Adults
While most hypospadias surgeries are performed in childhood, some adults seek surgery due to urinary issues or dissatisfaction with the appearance of their genitalia. Surgical outcomes in adults are comparable to those in children.
Society and Culture
Hypospadias can lead to emotional challenges, including anxiety and shame, particularly regarding social situations like school bathrooms. Understanding and addressing these emotional aspects are very important for holistic management of the condition.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What percentage of hypospadias cases are considered less severe?
Which of the following is a common characteristic associated with hypospadias?
What is the most frequent surgical method used to correct distal hypospadias?
Hypospadias is diagnosed primarily through:
What is the estimated occurrence rate of hypospadias in male births?
Which of the following complications can arise from hypospadias surgery?
Hypospadias can interfere with urination by causing:
Genetic and environmental factors are suspected in the cause of hypospadias, but which hypothesis focuses on epigenetic markers?
In the context of hypospadias surgery, what might be used preoperatively to increase penile size?
Which of the following emotions is often associated with individuals affected by hypospadias?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


