Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM), also known as glandular fever, is a common viral infectious disease primarily caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), a member of the herpesvirus family. It is colloquially referred to as "the kissing disease" due to its primary mode of transmission through saliva.
The disease mainly affects adolescents and young adults, presenting with symptoms such as fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue.
Signs and Symptoms
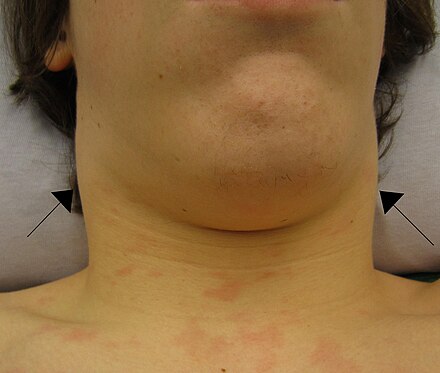
The clinical presentation of infectious mononucleosis varies with age. In children, the disease often produces mild flu-like symptoms or is asymptomatic. In adolescents and young adults, the disease typically presents with a characteristic triad of symptoms: fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes, particularly in the posterior cervical region. Patients may also experience profound fatigue, headaches, and abdominal pain with nausea or vomiting.
Symptoms usually resolve within 2-4 weeks, though fatigue can persist for months in some cases. A notable sign is pharyngitis with enlarged, pus-covered tonsils, and in about 50% of cases, petechiae may be observed on the palate. A maculopapular rash can occur, especially if the patient has been treated with amoxicillin or ampicillin.



Diagnosis
Diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis is primarily clinical, supported by laboratory tests. Physical examination may reveal an enlarged spleen and swollen lymph nodes. The heterophile antibody test (monospot test) is widely used but has limitations in sensitivity and specificity. Serologic tests for EBV-specific antibodies (IgM and IgG) provide a more accurate diagnosis, especially in the presence of suggestive symptoms and a negative heterophile antibody test.
A complete blood count (CBC) often shows increased lymphocytes, with more than 10% being atypical. Elevated hepatic transaminase levels can also support the diagnosis.


Treatment
The management of infectious mononucleosis is mainly supportive. Patients are advised to rest, stay hydrated, and use pain relief medications such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) and ibuprofen. Corticosteroids like prednisone may be prescribed in severe cases, particularly when there is significant throat pain or risk of airway obstruction. However, their routine use is controversial due to potential side effects.
Antiviral medications are generally not recommended for uncomplicated cases as they offer limited benefit and may cause adverse effects. Antibiotics are not effective against the virus but may be necessary for treating secondary bacterial infections. Notably, amoxicillin and ampicillin are contraindicated due to the high incidence of rash.
Patients should avoid contact sports and heavy physical activities for at least the first 3-4 weeks to reduce the risk of splenic rupture, which can be a serious complication.
Prognosis
Most individuals recover fully from infectious mononucleosis without long-term complications. However, serious complications, although rare, can include splenic rupture, neurological disorders, and hematologic abnormalities. The virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate, potentially causing asymptomatic viral shedding.


Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary cause of infectious mononucleosis?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of infectious mononucleosis?
Infectious mononucleosis is often referred to as "the kissing disease" because it is primarily transmitted through:
Which diagnostic test is widely used but has limitations in sensitivity and specificity for infectious mononucleosis?
A notable sign of pharyngitis in infectious mononucleosis is:
Which medication is contraindicated in the treatment of infectious mononucleosis due to the high incidence of rash?
Which complication is a concern that necessitates avoiding contact sports and heavy physical activities in the first 3-4 weeks of infectious mononucleosis?
In the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis, what finding is often observed in a complete blood count (CBC)?
Which age group is most commonly affected by infectious mononucleosis?
Which of the following is a serologic test used to confirm the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


