Laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx (voice box), typically presenting with a hoarse voice, fever, and pain. The condition is classified as acute if it lasts less than three weeks and chronic if it persists longer. It can arise from viral or bacterial infections, trauma, allergies, acid reflux, and other conditions.

Signs and Symptoms
The primary symptom of laryngitis is a hoarse voice. Other symptoms may include a dry or sore throat, cough, frequent throat clearing, increased saliva production, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), a sensation of swelling in the larynx, globus pharyngeus (feeling like there is a lump in the throat), cold or flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, fever, general muscle pain (myalgia), and shortness of breath, especially in children. Changes in voice quality can also occur, such as a lower or higher pitch, breathiness, quieter volume, and reduced range.
Causes
Laryngitis can be caused by infectious agents like viruses, bacteria, and fungi, as well as noninfectious factors such as trauma, allergies, and acid reflux. Acute laryngitis is often linked to viral infections like rhinovirus, influenza, and adenovirus. Bacterial causes include group A streptococcus and Streptococcus pneumoniae, among others. Fungal laryngitis, though less commonly diagnosed, can be caused by Histoplasma, Blastomyces, Candida, and other fungi. Trauma from excessive vocal use or medical procedures can also lead to acute laryngitis.
Chronic laryngitis may result from ongoing irritants such as smoking, acid reflux, and autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and sarcoidosis. Allergies and reflux are significant contributors, with gastro-oesophageal reflux potentially causing irritation and inflammation of the vocal folds.
Diagnosis
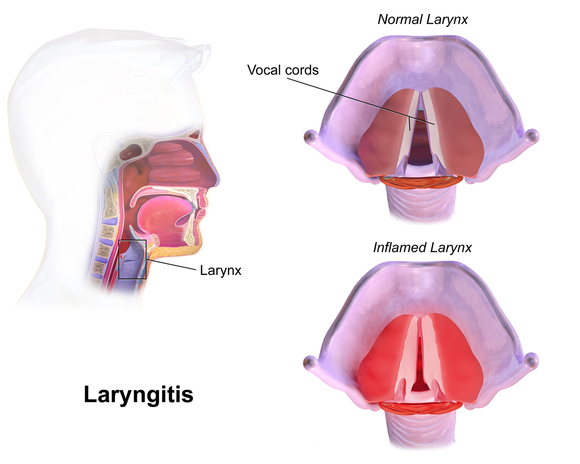
Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, symptom presentation, and visual examination through laryngoscopy or stroboscopy. Acute viral laryngitis is marked by hoarseness and upper respiratory symptoms lasting less than four weeks. Fungal laryngitis may require a biopsy and culture for confirmation. Laryngoscopy may reveal erythema, oedema, dilated blood vessels, and other tissue changes. Certain signs necessitate early referral, including difficulty swallowing, vocal stridor, ear pain, weight loss, smoking history, recent radiotherapy, and professional voice use.
Treatment
Treatment varies based on the type and severity of laryngitis. General measures include behaviour modification, hydration, and humidification. Vocal hygiene is very important and involves resting the voice, drinking water, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and limiting throat clearing.
For acute laryngitis, viral cases are managed with vocal rest, pain relief, and mucolytics. Antibiotics are generally not used for viral infections but may be prescribed for bacterial laryngitis, although their effectiveness is debated. Severe bacterial infections may require urgent intervention with humidification, corticosteroids, intravenous antibiotics, and nebulised adrenaline. Fungal laryngitis is treated with oral antifungal medications.
Chronic laryngitis treatment depends on the underlying cause. Reflux laryngitis is managed with behavioural changes, anti-reflux medications, and sometimes surgery. Allergic laryngitis may be treated with nasal steroids, immunotherapy, and antihistamines. Autoimmune-related laryngitis, such as mucous membrane pemphigoid, is managed with medications like cyclophosphamide and prednisolone. Sarcoidosis may require systemic corticosteroids or other treatments.
Prognosis
Acute laryngitis typically resolves within two weeks with appropriate treatment. Chronic laryngitis requires further investigation if symptoms persist beyond three weeks, with prognosis varying based on the underlying cause.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary symptom of laryngitis?
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of acute laryngitis?
What type of laryngitis is characterised by symptoms lasting more than three weeks?
Which of the following is a common fungal cause of laryngitis?
Which of the following is NOT a recommended general measure for treating laryngitis?
What is the most common cause of acute laryngitis?
Chronic laryngitis caused by acid reflux would typically be managed with:
Which diagnostic tool is commonly used to visually examine the larynx for laryngitis?
Which of the following symptoms would necessitate an early referral in a patient with laryngitis?
For viral laryngitis, which treatment is generally NOT recommended?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


