Malnutrition
Malnutrition is a medical condition that arises when an organism receives an imbalance of nutrients, either too few or too many, leading to health problems. It includes both undernutrition and overnutrition.
Undernutrition can result in stunted growth, wasting, and underweight, while overnutrition can lead to obesity. Both forms can coexist in the same communities, particularly in developing countries.

Prevalence
Globally, nearly one in three persons is affected by some form of malnutrition. Undernutrition is more prevalent in developing countries, especially among children under five. In 2021, 148.1 million children were stunted, 45 million were wasted, and 37 million were overweight or obese. Undernutrition is particularly severe in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.

Signs and Symptoms
In Children
Undernutrition in children can manifest as stunting, wasting, and underweight. Micronutrient deficiencies, such as vitamin A deficiency, can lead to significant health issues like blindness and increased mortality.
In Adults
Adults may experience undernutrition with symptoms like hair loss, swollen legs, and poor energy levels. Overnutrition can result in obesity and related conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Diagnosis
Undernutrition
Diagnosing undernutrition involves identifying signs like low weight-for-age, stunted growth, and micronutrient deficiencies. The Waterlow classification system, which uses weight-for-height and height-for-age measurements, is commonly used to diagnose undernutrition.
Overnutrition
Overnutrition is often diagnosed using body mass index (BMI). A BMI of 25 or more indicates overweight, while a BMI of 30 or more indicates obesity.
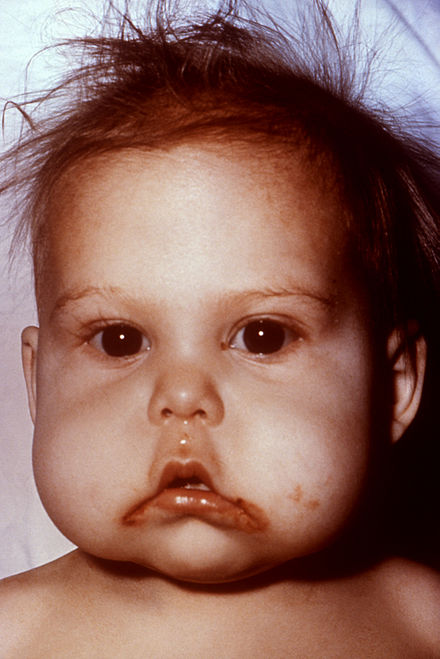
Kwashiorkor is characterised by oedema and liver enlargement due to inadequate protein intake. Marasmus results from severe energy deficiency, leading to extreme wasting and a gaunt appearance.
Causes and Risk Factors
Social and Political
Malnutrition is often linked to socio-economic factors like poverty, poor education, and lack of access to nutritious food. High food prices and inadequate agricultural practices can exacerbate the problem.
Diseases and Conditions
Chronic illnesses like HIV/AIDS and gastrointestinal diseases can lead to malnutrition. Infectious diseases that increase nutrient requirements, such as malaria and pneumonia, are also significant contributors.
Dietary Practices
A diet that lacks diversity or adequate breastfeeding can lead to undernutrition. Overnutrition is often caused by excessive consumption of high-calorie foods and a sedentary lifestyle.
Treatment
Improving Nutrition
Efforts to improve nutrition include promoting breastfeeding and providing ready-to-use therapeutic foods (RUTF). Nutritional counselling and supplementation with micronutrients like vitamin A and zinc are also effective.
Medical Management
Severe malnutrition often requires hospitalisation, where treatment focuses on managing low blood sugar, dehydration, and infections. Routine antibiotics are recommended due to the high risk of infection in malnourished individuals.

Therapeutic Foods
Specially formulated foods, like RUTF, are effective in treating moderate acute malnutrition. These foods are easy to store and do not require refrigeration, making them ideal for use in resource-poor settings.
Micronutrient Supplementation
Supplementing diets with essential vitamins and minerals can significantly improve health outcomes. For example, zinc supplementation can reduce the severity and duration of diarrhoea in malnourished individuals.

Managing Dehydration and Low Blood Sugar
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is very important for managing dehydration in malnourished individuals. Hypoglycaemia can be treated with a mixture of sugar and water, and keeping malnourished children warm can prevent hypothermia.
Epidemiology
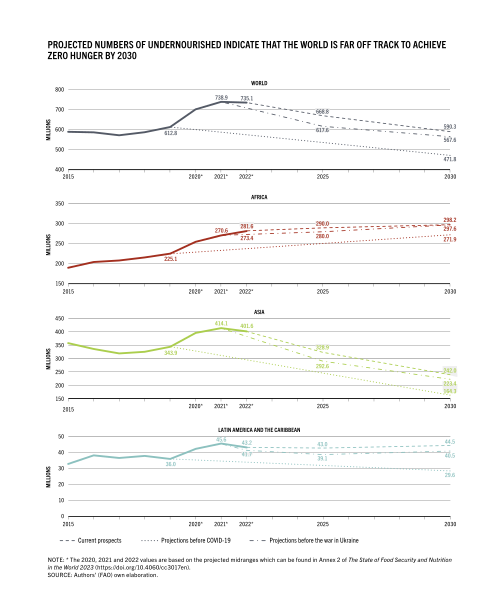
As of 2017, an estimated 821 million people were undernourished globally. Malnutrition is the leading cause of death in children under five, contributing to 45% of child mortality. Despite sufficient global food production, malnutrition persists due to socio-economic disparities and inadequate food distribution.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is malnutrition?
Which regions are most affected by undernutrition?
What is stunting in children?
How is overnutrition typically diagnosed?
What are common symptoms of undernutrition in adults?
Which of the following is NOT a cause of malnutrition?
What is kwashiorkor?
Which treatment is essential for managing dehydration in malnourished individuals?
What percentage of child mortality is contributed by malnutrition?
What is the role of ready-to-use therapeutic foods (RUTF) in treating malnutrition?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


