Ménière's Disease
Ménière's disease (MD), also known as Ménière's syndrome or idiopathic endolymphatic hydrops, is a disorder of the inner ear characterised by episodes of vertigo, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the affected ear.
Initially, it typically affects only one ear, but both ears may become involved over time. Episodes last from 20 minutes to a few hours and the frequency varies. The exact cause of MD is unclear, but it likely involves both genetic and environmental factors.
Signs and Symptoms
Ménière's disease is marked by recurrent episodes of vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss, and tinnitus. These episodes may be preceded by a headache and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Additional symptoms due to irregular reactions of the autonomic nervous system, such as nausea, vomiting, and sweating, are common and are typically symptoms of vertigo rather than MD itself. Some individuals may experience sudden falls without loss of consciousness, known as drop attacks.
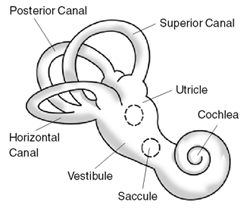
Causes and Mechanism
The precise cause of Ménière's disease is unknown, but theories include constrictions in blood vessels, viral infections, and autoimmune reactions. Genetic predisposition is seen in about 10% of cases. Symptoms are believed to occur due to increased fluid buildup in the labyrinth of the inner ear known as endolymphatic hydrops (EH). While EH is strongly associated with MD, not everyone with EH develops the disease. The balance (vestibular) system and the hearing (cochlea) system of the inner ear are affected, though sometimes only one system may show symptoms.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on the patient's symptoms and a hearing test. The 2015 diagnostic criteria define definite and probable MD. Definite MD includes two or more spontaneous episodes of vertigo, documented hearing loss, and fluctuating aural symptoms, while probable MD includes episodes of vertigo or dizziness and fluctuating aural symptoms, but may not meet the full criteria for definite MD.


Differential diagnoses include vestibular migraine, transient ischaemic attack (TIA), vestibular paroxysmia, recurrent unilateral vestibulopathy, vestibular schwannoma, and tumours of the endolymphatic sac. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be necessary to exclude TIA or stroke.
Management
There is no known cure for Ménière's disease, but various treatments can help manage the symptoms. More than 85% of patients improve through lifestyle changes, medical treatment, or minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Medications
During episodes, medications to reduce nausea and anxiety are used. Long-term treatments include diuretics to manage fluid buildup, though the evidence for their efficacy is limited. Chemical labyrinthectomy with gentamicin may be used in severe cases but carries the risk of further hearing loss. Glycopyrrolate has shown utility as a vestibular suppressant.
Diet
Reducing sodium intake is often advised, although its effectiveness is not well-supported by evidence. Eliminating potential migraine triggers like caffeine may also be recommended, but the evidence is weak.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy may not be useful early after the onset due to the fluctuating nature of the disease but can help with balance retraining in the long term.
Counselling
Psychological distress from vertigo and hearing loss can exacerbate the condition. Counselling, education, and relaxation techniques may help manage distress.
Surgery
Surgery is considered for uncontrolled or persistent cases. Endolymphatic sac surgery, including decompression or shunt insertion, may reduce dizziness, but the evidence is weak. Destructive surgeries like vestibular nerve labyrinthectomy and labyrinthectomy are irreversible and involve significant risks.
Poorly Supported Treatments
Betahistine is often used but lacks strong evidence. Transtympanic micropressure pulses and intratympanic steroids have insufficient evidence to support their efficacy. Alternative medicine such as acupuncture and herbal supplements are not supported by evidence.
Prognosis
Ménière's disease usually starts in one ear and may extend to both ears in about 30% of cases. Symptoms often progress over 5–15 years, resulting in mild disequilibrium, tinnitus, and moderate hearing loss in one ear.
Epidemiology
Ménière's disease accounts for 3 to 11% of dizziness diagnoses in neuro-otological clinics, with an annual incidence rate of about 15 cases per 100,000 people and a prevalence rate of about 218 per 100,000. The disease is more common in women, people of white ethnicity, and those with severe obesity. It is often comorbid with conditions such as arthritis, psoriasis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and migraine.
History
The condition is named after Prosper Menière, a French physician who described the main symptoms in 1861 and suggested a single disorder involving the balance and hearing organs in the inner ear. Diagnostic criteria have evolved over time, with significant updates in 1972, 1985, and 1995 to refine the definitions and degrees of the disease.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of Ménière's disease?
What percentage of Ménière's disease cases have a genetic predisposition?
Which diagnostic tool is often used to exclude transient ischaemic attack (TIA) or stroke in patients suspected of having Ménière's disease?
What is the term for sudden falls without loss of consciousness experienced by some individuals with Ménière's disease?
Which of the following is a minimally invasive procedure sometimes used to treat Ménière's disease?
Which medication is used for vestibular suppression in Ménière's disease?
What proportion of patients with Ménière's disease may experience improvement through lifestyle changes or medical treatment?
Which dietary change is commonly recommended for patients with Ménière's disease, despite limited evidence?
Which of the following conditions is NOT commonly comorbid with Ménière's disease?
In what year did Prosper Menière describe the main symptoms of the disease that now bears his name?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


