Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL). It is closely associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
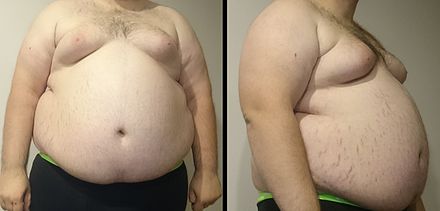
Signs and Symptoms
The key sign of metabolic syndrome is central obesity, also known as visceral or apple-shaped adiposity, characterised by adipose tissue accumulation predominantly around the waist and trunk. Other signs include high blood pressure, decreased fasting serum HDL cholesterol, elevated fasting serum triglyceride level, impaired fasting glucose, insulin resistance, or prediabetes.
Associated conditions include hyperuricaemia, fatty liver progressing to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, polycystic ovarian syndrome in women, erectile dysfunction in men, and acanthosis nigricans.
Neck Circumference
Neck circumference is a simple and reliable indicator of upper-body subcutaneous fat accumulation. Neck circumference of more than 40.25 cm (15.85 in) for men and more than 35.75 cm (14.07 in) for women is considered high-risk for metabolic syndrome. Increased neck circumference has been associated with a higher risk of severe complications in COVID-19 patients.
Complications
Metabolic syndrome can lead to several serious and chronic complications, including type-2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, stroke, kidney disease, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Moreover, it significantly increases the risk of surgical complications across most types of surgery.
Causes
The pathophysiology of metabolic syndrome is complex and multifactorial. Key risk factors include diet, genetics, ageing, sedentary behaviour, disrupted sleep patterns, mood disorders, psychotropic medication use, and excessive alcohol use. Chronic stress may disrupt the hormonal balance of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, contributing to insulin resistance and visceral adiposity.
Obesity, particularly central obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle are significant contributors. The syndrome is also more prevalent with ageing and among certain ethnic groups.
Diagnosis
NCEP
The U.S. National Cholesterol Education Programme Adult Treatment Panel III (2001) defines metabolic syndrome by the presence of at least three of the following criteria:
- Central obesity: waist circumference ≥ 102 cm (male), ≥ 88 cm (female)
- Dyslipidaemia: TG ≥ 1.7 mmol/L
- Dyslipidaemia: HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (male), < 50 mg/dL (female)
- Blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg
- Fasting plasma glucose ≥ 6.1 mmol/L
2009 Interim Joint Statement
This statement harmonises the definition of metabolic syndrome, requiring three or more of the following:
- Elevated waist circumference with population-specific definitions
- Elevated triglycerides (≥ 150 mg/dL)
- Reduced HDL-C (≤40 mg/dL in males, ≤50 mg/dL in females)
- Elevated blood pressure (≥130/85 mm Hg)
- Elevated fasting glucose (≥100 mg/dL)
WHO
The World Health Organisation (1999) requires the presence of diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance, or insulin resistance, AND two of the following:
- Blood pressure ≥ 140/90 mmHg
- Dyslipidaemia: TG ≥ 1.695 mmol/L and HDL cholesterol ≤ 0.9 mmol/L (male), ≤ 1.0 mmol/L (female)
- Central obesity: waist:hip ratio > 0.90 (male); > 0.85 (female), or BMI > 30 kg/m2
- Microalbuminuria: urinary albumin excretion ratio ≥ 20 μg/min or albumin:creatinine ratio ≥ 30 mg/g
Management
Medications
Individual disorders that compose metabolic syndrome are treated separately. Diuretics and ACE inhibitors may be used to treat hypertension, while various cholesterol medications may address abnormal LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and HDL cholesterol levels.
Diet
Dietary carbohydrate restriction can reduce blood glucose levels, aid in weight loss, and decrease the need for medications prescribed for metabolic syndrome.
Epidemiology
Approximately 20–25% of the world's adult population has metabolic syndrome. In the U.S., about 34% of adults are affected, with higher prevalence observed in those over the age of 50 and among certain ethnic groups.
History
The association of diabetes with hypertension and hyperuricaemia was first reported in 1921. The term metabolic syndrome was used in the late 1950s to describe a constellation of risk factors for cardiovascular disease, with insulin resistance proposed as the underlying factor in 1988 by Gerald M. Reaven.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the key sign of metabolic syndrome?
Which of the following neck circumference values indicate a high risk for metabolic syndrome in men?
Which of the following is NOT a criterion for metabolic syndrome according to the NCEP definition?
According to the 2009 Interim Joint Statement, what is the threshold for elevated fasting glucose to diagnose metabolic syndrome?
Which of the following complications is NOT associated with metabolic syndrome?
What percentage of the world's adult population is estimated to have metabolic syndrome?
Which medication type is commonly used to treat hypertension in metabolic syndrome patients?
Which of the following factors is a significant contributor to metabolic syndrome?
According to WHO, which of the following is required in addition to two other criteria to diagnose metabolic syndrome?
Who proposed insulin resistance as the underlying factor for metabolic syndrome in 1988?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


