Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterised by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. It is the most common form of arthritis, affecting about 237 million people worldwide as of 2015.
OA primarily affects joints, leading to symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion, which typically develop slowly over years.
Signs and Symptoms
The main symptoms of osteoarthritis include joint pain and stiffness, often exacerbated by prolonged activity and relieved by rest. Stiffness is most common in the morning and typically lasts less than 30 minutes after beginning daily activities but can return after periods of inactivity.
Other symptoms may include joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and a crackling noise (crepitus) when the affected joint is moved. OA commonly affects the hands, feet, spine, and large weight-bearing joints such as the hips and knees.
In advanced stages, hard bony enlargements, known as Heberden's nodes (distal interphalangeal joints) and Bouchard's nodes (proximal interphalangeal joints), may form, limiting finger movement.


Causes
OA results from mechanical stress on the joint and low-grade inflammatory processes. Risk factors include previous joint injury, abnormal joint or limb development, and inherited factors.
Overweight individuals, those with legs of different lengths, and those in jobs with high levels of joint stress are at greater risk. OA is correlated with age, and changes in sex hormone levels may play a role, particularly in post-menopausal women.
Pathophysiology
OA involves gross cartilage loss and damage to other joint tissues, including thickening and fibrosis of ligaments and menisci damage. New bone outgrowths, or osteophytes, form at joint margins.
The subchondral bone becomes thicker and less mineralised. Pain in OA joints is often related to thickened synovium and subchondral bone lesions.


Diagnosis
Diagnosis of OA is based on history and clinical examination, with X-rays used to confirm the diagnosis. Typical X-ray changes include joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis, subchondral cyst formation, and osteophytes.
Synovial fluid analysis can help differentiate OA from other types of arthritis.

Management
Treatment for OA includes lifestyle modifications, pain management, and in severe cases, surgery. Weight loss and exercise are very important for long-term management.
Pain medications such as paracetamol and NSAIDs are commonly used. For those with severe symptoms, joint replacement surgery may be considered.
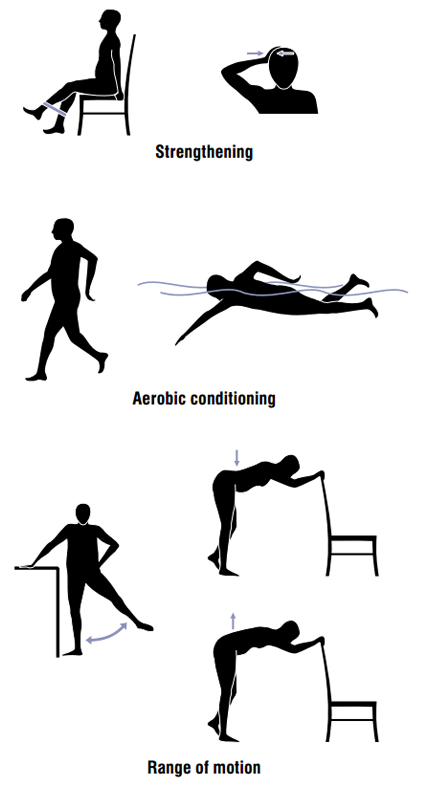
Exercise
Exercise, particularly low-impact activities like walking or swimming, helps maintain joint function and alleviate symptoms. Supervised exercise programmes can improve adherence and outcomes.
Physical Measures
Physical therapies, including aquatic therapy, functional, gait, and balance training, may help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Knee braces and insoles may offer relief for some individuals, though their effectiveness varies.
Medications
Paracetamol is the first-line treatment for pain, with NSAIDs used for more severe symptoms. Intra-articular steroid injections provide short-term pain relief.
Opioids are generally not recommended due to their side effects and risk of addiction.
Surgery
Joint replacement surgery, particularly for knees and hips, can be effective for those with significant OA symptoms that do not respond to conservative treatments. Other surgical options include arthrodesis and osteotomy, depending on the joint affected.


Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which of the following is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis?
Which joints are most commonly affected by osteoarthritis?
Which of the following factors is NOT a known risk factor for osteoarthritis?
In osteoarthritis, which of the following findings is typically seen on an X-ray?
What is the primary pathological feature of osteoarthritis?
Which of the following is the first-line treatment for pain management in osteoarthritis?
Which physical activity is recommended for patients with osteoarthritis to maintain joint function and alleviate symptoms?
Which of the following surgical options is considered for severe osteoarthritis when conservative management fails?
What is a characteristic feature of osteoarthritis that differentiates it from rheumatoid arthritis?
Which of the following is an appropriate non-pharmacological intervention for osteoarthritis?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


