Otitis Externa
Otitis externa, also known as swimmer's ear, is an inflammation of the ear canal, often presenting with ear pain, swelling, and occasionally decreased hearing. Pain typically intensifies with movement of the outer ear, and high fever is rare except in severe cases. The condition can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than three months). Acute cases are generally caused by bacterial infections, while chronic cases often result from allergies or autoimmune disorders.
Signs and Symptoms

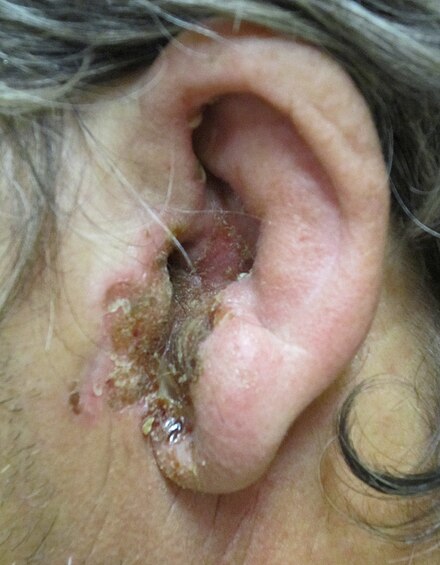
The predominant symptom of acute otitis externa is tenderness of the pinna, which worsens when the outer ear is touched or gently pulled. Additionally, pushing the tragus (the tablike portion of the auricle in front of the ear canal) typically causes pain, aiding in diagnosis. Other symptoms include ear discharge and itchiness. When swelling and discharge block the ear canal, temporary conductive hearing loss may occur.
Causes
Otitis externa develops when germs infect the skin of the ear canal, often facilitated by impairments in skin integrity. Healthy skin usually resists infection unless exposed to a high concentration of pathogens. However, chronic skin conditions like atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, or trauma can predispose to infection. Fungal infections, or otomycosis, can vary in severity, often exacerbated by prolonged use of steroid-containing antibacterial ear drops.
Swimming and Other Factors
Swimming in polluted water or water trapped in the ear after a shower can lead to otitis externa, particularly in humid climates. Prolonged swimming can saturate the ear canal skin, making it susceptible to damage from cleaning attempts. Constriction of the ear canal from bone growth (Surfer’s ear) or occupational exposure in saturation divers can also lead to infection.
Objects in Ear
Using objects like cotton swabs to clear the ear canal can cause skin breaks, allowing infection to develop. Once inflamed, the condition can worsen from further scratching or water exposure.
Infections
Most cases are due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, with Candida albicans and Aspergillus species being common fungal pathogens.
Diagnosis
Inspection reveals a red and swollen ear canal in well-developed cases, with the canal appearing eczema-like. Pain with manipulation of the outer ear helps establish the diagnosis. In severe cases, lymph node swelling beneath the ear may occur. Early diagnosis is challenging as the ear may appear normal except for pain with manipulation.
Prevention
Preventive strategies include avoiding the insertion of objects into the ear canal, using ear dryers or acetic acid drops after swimming, and avoiding swimming in polluted water. Earplugs during swimming or shampooing can help but must be used carefully to avoid scratching the ear canal.
Treatment
Medications
Treatment involves acidifying and drying agents, with Burow’s solution being effective against both bacterial and fungal infections. Ear drops are the mainstay of treatment, often containing antibiotics, antifungals, and anti-inflammatory steroids. Oral antibiotics should be reserved for severe cases involving soft tissue swelling.
Cleaning
Removing debris from the ear canal promotes medication effectiveness and shortens recovery time. In cases of severe swelling, an ear wick may be used to ensure medication reaches the infected area.
Prognosis
Otitis externa typically responds well to treatment, but complications can occur, particularly in individuals with diabetes or compromised immune systems. These complications include chronic otitis externa, necrotising external otitis, and skull base osteomyelitis.
Necrotising External Otitis
This severe form occurs mainly in elderly diabetics, beginning as an infection of the external ear canal and potentially spreading to the bony ear canal and soft tissues. It requires oral or intravenous antibiotics and diabetes control. Unrecognised and untreated, it can result in cranial nerve palsies and significant morbidity. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a controversial adjunctive treatment.
Epidemiology
Otitis externa is common, affecting 1-3% of people annually, with a higher incidence in warm, wet climates. It is most frequent among children aged seven to twelve and the elderly, occurring equally in males and females.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary symptom of acute otitis externa?
Which bacteria are most commonly associated with acute otitis externa?
Which of the following is NOT commonly a cause of chronic otitis externa?
What preventive measure can help reduce the risk of otitis externa in swimmers?
Which statement is true about the treatment of otitis externa?
What condition is a severe form of otitis externa that may affect elderly diabetics?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typical of otitis externa?
What can be used to ensure medication reaches the infected area in cases of severe ear canal swelling?
Which of the following factors can predispose someone to otitis externa?
What is the best method for diagnosing otitis externa?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


