Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) refers to a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower oesophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer.
Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, belching, vomiting, blood in the stool, weight loss, weight gain, bloating, and loss of appetite. Duodenal ulcers typically cause upper abdominal pain that improves with eating, while gastric ulcers may cause pain that worsens with eating.
A third of older patients may be asymptomatic.
Complications can include bleeding, perforation, and gastric obstruction. Bleeding occurs in approximately 15% of cases, presenting as hematemesis (vomiting blood) or melena (tarry, foul-smelling stools).


Causes
Helicobacter pylori
The most common causes of PUD are infection with Helicobacter pylori and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). H. pylori bacteria cause inflammation and damage to the stomach lining by producing urease, which creates an alkaline environment suitable for its survival.
NSAIDs
NSAIDs, such as aspirin, can increase the risk of PUD by four times due to their inhibition of prostaglandins that protect the stomach lining.
Other Causes
Other causes include smoking, stress from severe illness, Behçet's disease, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, Crohn's disease, and liver cirrhosis. Contrary to popular belief, diet and spicy foods play a minor role in ulcer formation.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and confirmed through endoscopy or barium swallow tests. For H. pylori detection, methods include the urea breath test, stool antigen test, blood antibody test, and biopsy during endoscopy.
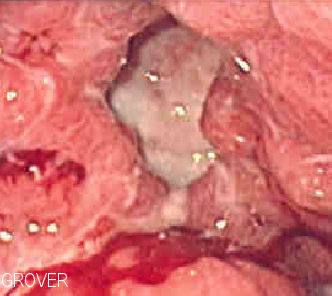
Classification
Peptic ulcers are classified by location: duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, esophageal ulcers, and Meckel's diverticulum ulcers. They can also be classified based on their appearance and associated conditions.
Management
Medications
Treatment involves stopping NSAIDs, smoking, and alcohol consumption, along with medications to reduce stomach acid, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers. H. pylori infections are treated with a combination of antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin, clarithromycin) and PPIs.

Complications Management
For bleeding ulcers, endoscopy can be used for cauterisation or clipping, and surgery may be required if endoscopy fails. In cases of perforation or obstruction, surgical intervention is often necessary.
Epidemiology
Peptic ulcers affect around 4% of the population, with approximately 87.4 million new cases worldwide in 2015. The prevalence decreases with the use of effective treatments and rational NSAID use.
Mortality has also declined significantly, from 327,000 deaths in 1990 to 267,500 in 2015.


Historical Context
The link between H. pylori and peptic ulcers was established by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren in the 1980s, earning them the Nobel Prize in 2005.
This discovery revolutionised the understanding and treatment of peptic ulcer disease.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the most common cause of peptic ulcer disease?
Which of the following medications is commonly used to reduce stomach acid in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease?
A patient with a duodenal ulcer typically experiences pain that is:
Which diagnostic test is considered the gold standard for confirming the presence of a peptic ulcer?
What complication of peptic ulcer disease is characterised by sudden, intense abdominal pain and requires immediate surgery?
Which of the following bacteria is a major causative factor for peptic ulcers and can be detected using a urea breath test?
A gastric ulcer is most often localised on which part of the stomach?
What is the typical first-line treatment for an H. pylori infection causing a peptic ulcer?
Which symptom is more commonly associated with a gastric ulcer compared to a duodenal ulcer?
In the event of a bleeding peptic ulcer, which treatment is typically first attempted?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


