Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. It is commonly caused by infections due to bacteria, viruses, or less commonly fungi and parasites. The condition can present with various symptoms and severity, often requiring clinical evaluation and imaging for diagnosis.

Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain. In elderly individuals, confusion may be the most prominent sign. Children under five typically show fever, cough, and fast or difficult breathing. Other symptoms may include fatigue, sputum production, and, in severe cases, blue-tinged skin or convulsions.

Causes
Pneumonia can be caused by various pathogens:
Bacteria
The most common bacterial cause is Streptococcus pneumoniae, responsible for nearly 50% of cases. Other bacteria include Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.

Viruses
Viruses account for about one-third of pneumonia cases in adults and 15% in children. Common viruses include rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, and influenza viruses.
Fungi and Parasites
Fungal pneumonia is more common in immunocompromised individuals and is typically caused by Histoplasma capsulatum and Pneumocystis jiroveci. Parasitic infections causing pneumonia are rare but can occur, especially in people returning from travel or immigrants.
Diagnosis
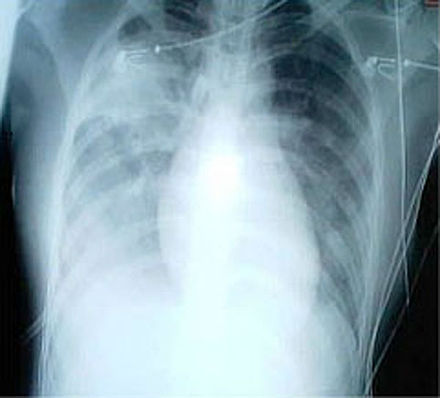
Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical signs, physical examination, and imaging studies like chest X-rays. Blood tests and sputum cultures can also help identify the causative pathogen, though often the specific agent is not determined.

Imaging
Chest radiographs are frequently used in diagnosis. CT scans can provide additional information in indeterminate cases or those with unclear radiographs. Lung ultrasound may also be useful.

Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
Bacterial Pneumonia
Antibiotics are the primary treatment, with the choice of antibiotic depending on the patient's age, health status, and the infection's origin (community-acquired or hospital-acquired).
Viral Pneumonia
Neuraminidase inhibitors may be used to treat influenza-related pneumonia. Antibiotics might be recommended to prevent secondary bacterial infections.
Prevention
Prevention strategies include vaccination against influenza and Streptococcus pneumoniae, smoking cessation, improving air quality, and practising good hand hygiene. Vaccines have significantly reduced the incidence of pneumonia caused by vaccine-preventable pathogens.
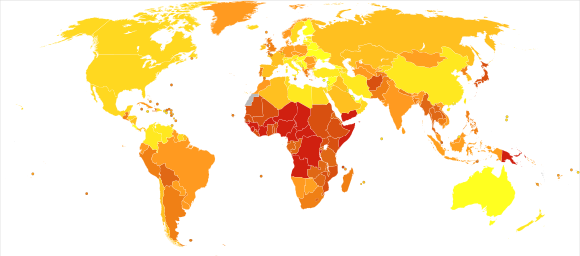
Complications
Complications of pneumonia can include pleural effusion, lung abscess, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Severe cases may require intensive care, including mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary area of the lungs affected by pneumonia?
Which bacterium is the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia?
What is a common symptom of pneumonia in elderly individuals?
Which imaging technique is most frequently used in the diagnosis of pneumonia?
Which pathogen is more likely to cause pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals?
What is the primary treatment for bacterial pneumonia?
What is a severe complication of pneumonia that may require intensive care?
Which virus is a common cause of viral pneumonia?
Which prevention strategy has significantly reduced the incidence of pneumonia caused by vaccine-preventable pathogens?
What is the typical cause of fungal pneumonia?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


