Polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly known as polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. It primarily affects children under five years of age, although it can also impact adults. The disease can range from asymptomatic to severe, including permanent paralysis and death in extreme cases.

Signs and Symptoms
Polio presents in various forms:
- Asymptomatic: About 72% of cases show no symptoms.
- Minor Illness: Around 24% of cases exhibit minor symptoms such as sore throat and fever, which resolve in one to two weeks.
- Nonparalytic Aseptic Meningitis: Approximately 1–5% of cases progress to this form, showing symptoms like headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia.
- Paralytic Poliomyelitis: Occurs in 0.1–0.5% of cases, leading to muscle weakness and acute flaccid paralysis. Paralysis affects the legs most commonly but can also impact the head, neck, and diaphragm.

Cause and Transmission
Polio is caused by the poliovirus, a member of the genus Enterovirus. It spreads primarily via the faecal–oral route but can also transmit through oral–oral routes. The virus is highly contagious and can be excreted in faeces for up to six weeks post-infection. Poor hygiene significantly increases the risk of transmission.

Pathophysiology
Poliovirus enters through the mouth, infecting cells in the pharynx and intestinal mucosa before spreading to the tonsils, lymphoid tissue, and eventually the bloodstream. In about 1% of cases, it invades the central nervous system (CNS), causing inflammation and potentially leading to paralytic poliomyelitis. The virus targets motor neurons, resulting in muscle atrophy and paralysis.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical signs of acute flaccid paralysis and confirmed through laboratory tests. The presence of poliovirus in stool samples or pharyngeal swabs, detected using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or genomic sequencing, is definitive.
Prevention
Vaccination
Two types of vaccines are used:
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV): Developed by Jonas Salk, it is given by injection and induces immunity after three doses.
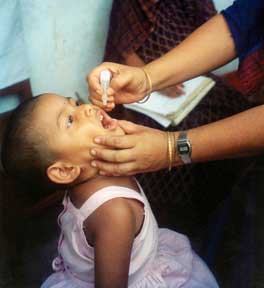
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV): Developed by Albert Sabin, it contains live attenuated virus and is administered orally. Although effective, it carries a risk of vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV).
Treatment
There is no cure for polio; treatment focuses on supportive care. This includes pain relief, antibiotics to prevent secondary infections, and long-term rehabilitation such as physical therapy and orthopaedic surgery. Mechanical ventilation, historically provided by iron lungs, may be necessary for those with respiratory involvement.
Prognosis and Complications
Recovery varies: some patients recover completely, while others may have permanent paralysis. Complications include skeletal deformities, muscle atrophy, and joint contractures. Post-polio syndrome (PPS) can occur decades later, causing muscle weakness and fatigue.

Epidemiology and Eradication Efforts
Polio was once a global epidemic, but vaccination campaigns have significantly reduced its prevalence. The Global Polio Eradication Initiative aims to eliminate the disease entirely. As of recent reports, wild poliovirus remains endemic in only a few countries, including Afghanistan and Pakistan.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary age group affected by poliomyelitis?
What percentage of polio cases are asymptomatic?
Which form of polio leads to symptoms like headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia?
What is the primary route of transmission for poliovirus?
Which vaccine for polio is administered orally?
In cases of paralytic poliomyelitis, which body part is most commonly affected by paralysis?
What is the definitive method for diagnosing polio?
Which of the following is a common complication that can occur decades after the initial polio infection?
Which countries remain endemic with wild poliovirus as of recent reports?
The Global Polio Eradication Initiative aims to:
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


