Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent endocrine disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is characterised by a variety of symptoms due to hormonal imbalances, including irregular menstrual periods, hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries.
The disorder's name originates from the cysts that may form on the ovaries, although not all affected women have these cysts.
Signs and Symptoms
Women with PCOS may experience a range of symptoms including irregular or absent menstrual periods, heavy menstrual bleeding, excess hair growth (hirsutism), acne, pelvic pain, and difficulty getting pregnant. Other symptoms include patches of thick, darker, velvety skin known as acanthosis nigricans, weight gain, and androgenic alopecia (hair thinning or loss). Associated conditions include type 2 diabetes, obesity, obstructive sleep apnoea, heart disease, mood disorders, and endometrial cancer.

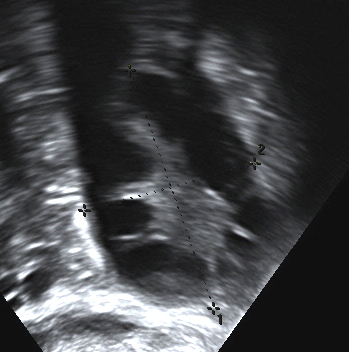
Polycystic ovary: The condition may lead to enlarged ovaries with multiple small cysts.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of PCOS typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. According to the Rotterdam criteria, a diagnosis can be made if two of the following three criteria are met: oligoovulation or anovulation, excess androgen activity, and polycystic ovaries visible on gynecologic ultrasound.
Differential Diagnosis
It's essential to differentiate PCOS from other causes of irregular menstruation and hirsutism, such as adrenal hyperplasia, hypothyroidism, hyperprolactinaemia, and androgen-secreting tumours.
Assessment and Testing
A comprehensive assessment includes obtaining a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. Laboratory tests typically measure serum androgen levels, while gynecologic ultrasonography can reveal the presence of polycystic ovaries.

Pathogenesis
PCOS is thought to develop when the ovaries produce excessive amounts of androgenic hormones, particularly testosterone, due to excessive luteinizing hormone (LH) release or high insulin levels in the blood. Insulin resistance is common among women with PCOS, contributing to the hormonal imbalances that characterise the syndrome.
Treatment
PCOS management focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and regular exercise, are fundamental. Medications include birth control pills to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and manage acne and hirsutism. Metformin is commonly prescribed to improve insulin resistance, and fertility treatments include clomiphene citrate and letrozole.
Medications
Oral contraceptives are often used to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels. Metformin is used to address insulin resistance and can sometimes restore regular ovulation. Anti-androgens like spironolactone may be used to manage hirsutism and acne.
Infertility Treatment
For women struggling with infertility due to PCOS, treatments include weight loss, ovulation induction with clomiphene or letrozole, and assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilisation (IVF). Surgical options such as ovarian drilling may be considered in some cases.
Cosmetic Procedures
For hirsutism, cosmetic procedures like laser hair removal, electrolysis, and topical treatments may be beneficial. Acne can be treated with standard acne medications, often in conjunction with hormonal treatments.
Associated Conditions
PCOS is linked to several metabolic and cardiovascular risks, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidaemia. Mental health issues such as depression and anxiety are also more common in women with PCOS.
Epidemiology
PCOS is the most common endocrine disorder among women of reproductive age, with prevalence rates ranging from 2% to 20% depending on diagnostic criteria. It's estimated to affect up to 26% of certain populations, with varying prevalence across different countries.
PCOS was first described in 1935 by American gynaecologists Stein and Leventhal, and it remains a significant cause of infertility and menstrual irregularities in women worldwide.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) primarily characterised by?
Which diagnostic criteria are used to diagnose PCOS according to the Rotterdam criteria?
Which medication is commonly prescribed to improve insulin resistance in women with PCOS?
Which symptom is NOT typically associated with PCOS?
Which of the following is a common complication associated with PCOS?
What is the primary focus of PCOS management?
Which fertility treatment might be considered for women with PCOS?
What are the typical laboratory tests used to diagnose PCOS?
Which lifestyle change is fundamental in managing PCOS?
Which of the following is NOT a common treatment for hirsutism in women with PCOS?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


