Rash
A rash is a change in the skin that affects its colour, appearance, or texture. Rashes can be localised or widespread and may cause the skin to change colour, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracked, blistered, or swollen, and may also be painful. The causes and treatments for rashes vary widely, and accurate diagnosis takes into account the rash's appearance, other symptoms, possible exposures, occupation, and familial occurrence.
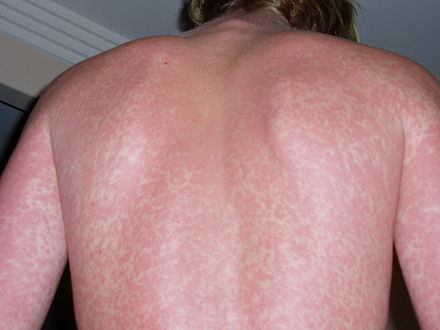
Differential Diagnosis
Common causes of rashes include food allergies, medication side effects, anxiety, allergies to substances like food, dyes, medicines, insect stings, and metals. Contact with irritants, fungal infections such as ringworm, skin diseases like eczema or acne, sun exposure, heat, friction, secondary syphilis, and poor personal hygiene are also frequent causes.
Uncommon causes include autoimmune disorders like psoriasis, lead poisoning, pregnancy, repeated scratching, Lyme disease, scarlet fever, and COVID-19.
Conditions and Symptoms
- Acne vulgaris: Comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules on the face, chest, and back.
- Acne rosacea: Flushed appearance or redness on the cheeks, chin, forehead, or nose.
- Boil: Painful red bump or cluster of bumps anywhere on the body.
- Cellulitis: Red, tender, and swollen areas of skin, usually around a cut or scrape.
- Insect bite: Red and/or itchy bumps, which can be sprinkled randomly anywhere on the body.
- Erythema migrans (Lyme disease): Expands over days or weeks to 5–70 cm, typically in areas like the armpit, groin, back of the knee, trunk, under clothing straps, or in children's hair, ear, or neck.
Diagnostic Approach
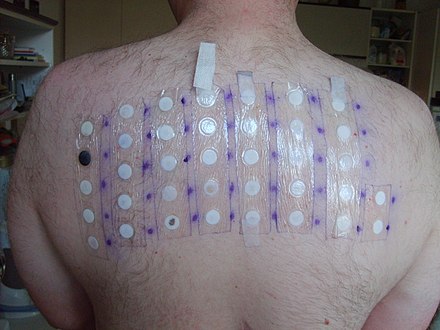
Evaluating a rash can be complex due to the numerous potential causes. An accurate assessment requires a thorough history, including medications, occupation, and travel history, along with a complete physical examination.
Key examination points include:
- Appearance: Purpuric (vasculitis and meningococcal disease), fine and sandpaper-like (scarlet fever), circular lesions with central depression (molluscum contagiosum, smallpox), plaques with silver scales (psoriasis).
- Distribution: For example, the rash of scarlet fever forms bright red lines in the neck, armpits, and groins (Pastia's lines); chickenpox vesicles follow body hollows.
- Symmetry: Herpes zoster typically affects only one side of the body without crossing the midline.
A patch test may be ordered to identify allergens.
Treatment
Treatment varies based on the specific rash diagnosed. Common rashes can often be treated with steroid topical creams like hydrocortisone or non-steroidal treatments, many of which are available over the counter in the UK. However, steroid creams may be ineffective for severe cases due to their limited skin penetration.
In conclusion, understanding the various causes, symptoms, and treatments of rashes is very important for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, especially in a professional setting.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is a common cause of rashes?
Which of the following is a symptom of cellulitis?
What kind of rash might you expect with secondary syphilis?
Which of these conditions is characterised by comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules?
Which diagnostic tool may be used to identify allergens causing a rash?
In the evaluation of a rash, which factor is NOT typically considered?
Which condition is indicated by expanding lesions that can reach 5–70 cm?
What is a possible treatment for common rashes?
Which of the following rashes is typically symmetrical?
What is a characteristic distribution of the rash caused by scarlet fever?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


