Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammatory disease that can affect the heart, joints, skin, and brain, typically developing two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection. It frequently affects children aged 5-14 and can lead to severe complications such as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), heart failure, and atrial fibrillation.

Signs and Symptoms
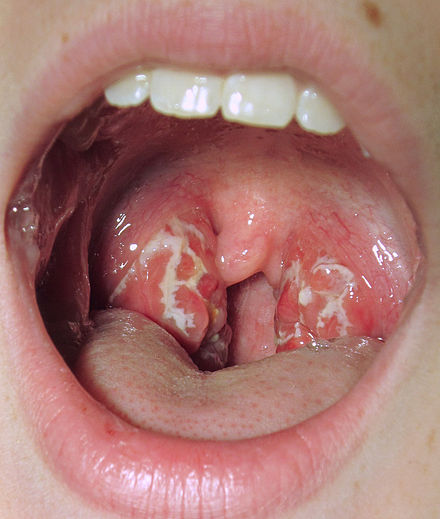
Rheumatic fever manifests with fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and occasionally erythema marginatum, a non-itchy rash. The heart is involved in about half of the cases, which can eventually lead to valve damage and heart failure.
Pathophysiology
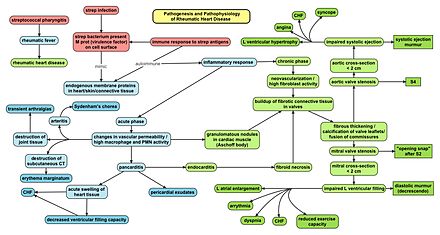
Rheumatic fever follows an untreated infection by Streptococcus pyogenes. The immune system's antibodies may mistakenly attack the body's own tissues, particularly the heart and joints, leading to inflammation. This is due to the similarity between bacterial antigens and cardiac proteins.

Rheumatic Heart Disease
Chronic RHD involves repeated inflammation and repair of the heart valves, leading to fibrosis and scarring. Molecular mimicry and genetic predisposition are key factors, with CD4+ T cells playing a major role in the autoimmune response.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on the presence of signs and symptoms along with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection. The Jones criteria, which include major and minor clinical findings, are commonly used. Echocardiography is preferred for detecting early signs of heart involvement.
Major Criteria
- Polyarthritis: Migrating inflammation of large joints.
- Carditis: Can involve pericardium, myocardium, and endocardium, diagnosed clinically or via echocardiography.
- Subcutaneous nodules: Painless, firm collections over bones or tendons.
- Erythema marginatum: Long-lasting reddish rash.
- Sydenham's chorea: Involuntary rapid movements of the face and arms.
Minor Criteria
- Arthralgia: Joint pain without swelling.
- Fever: ≥38.5°C in low-incidence populations.
- Raised ESR or CRP: Indicators of inflammation.
- Prolonged PR interval on ECG: After accounting for age variability.
Prevention
Preventing rheumatic fever involves promptly treating streptococcal throat infections with antibiotics. Improved sanitation and reduced overcrowding are also very important preventive measures. For those with a history of RF, long-term antibiotic prophylaxis is recommended to prevent recurrence.
Treatment
Infection
Penicillin is the antibiotic of choice for treating streptococcal pharyngitis. Monthly injections of long-acting penicillin may be required for up to 40 years in cases with carditis.
Inflammation
Historically, high doses of aspirin were used, but due to side effects, alternatives like naproxen are now considered. Corticosteroids may be used in severe cases or if there's an allergy to NSAIDs.
Heart Failure
Management of severe carditis or heart failure includes ACE inhibitors, diuretics, beta-blockers, and possibly corticosteroids for their anti-inflammatory effects.


Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What age group is most frequently affected by rheumatic fever?
What is the most common cause of rheumatic fever?
Which of the following is NOT a major criterion for diagnosing rheumatic fever according to the Jones criteria?
Which medication is commonly used for long-term antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with a history of rheumatic fever?
What type of valve damage is characteristic of rheumatic heart disease?
Which statement about Sydenham's chorea is true?
What is the preferred imaging technique for detecting early signs of rheumatic heart disease?
Which of the following is a minor criterion for diagnosing rheumatic fever?
What is the primary factor in the pathophysiology of rheumatic fever?
What is the main treatment for acute inflammation in rheumatic fever patients who cannot tolerate NSAIDs?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


