Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an infection caused by Salmonella bacteria, commonly associated with food poisoning. This essay covers its signs and symptoms, causes, prevention, and treatment, with a focus on its relevance to general medicine and surgery.
Signs and Symptoms
Enteritis
Salmonellosis primarily manifests as enteritis, characterised by diarrhoea, fever, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. Symptoms typically appear 12 to 72 hours after infection and last four to seven days. Diarrhoea is usually watery and non-bloody but can become mucoid and bloody. Most cases resolve without treatment, but severe dehydration may require hospitalisation for intravenous fluids and symptomatic relief.

Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever occurs when Salmonella bacteria enter the lymphatic system, leading to systemic infection. Symptoms include vomiting, diarrhoea, upset thermal regulation, and in severe cases, hypovolaemic or septic shock. This condition necessitates prompt antibiotic treatment.
Long-term Effects
Post-infection, some individuals may develop reactive arthritis or chronic arthritis. Those with sickle-cell anaemia are at higher risk for osteomyelitis. Additionally, salmonellosis can lead to irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease.
Causes
Salmonellosis is primarily caused by consuming contaminated food, water, or milk. Poor kitchen hygiene, particularly in institutional kitchens, exacerbates the risk. Pets, especially reptiles and amphibians, can also be carriers of Salmonella.
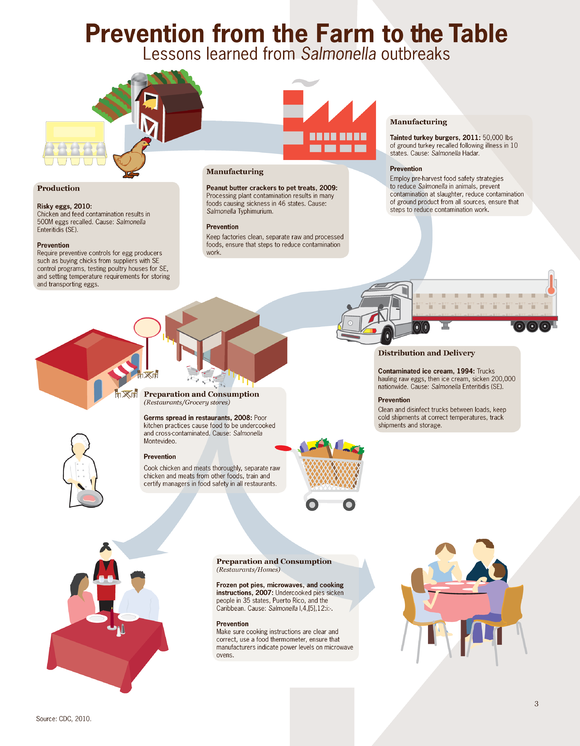
Prevention
Efforts to prevent salmonellosis focus on proper food handling and cooking. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends cooking food to 145–165°F (63–74°C) and boiling liquids when reheating. Freezing can kill some Salmonella but is not wholly reliable. Vaccination of chickens has significantly reduced salmonellosis in the UK.
Diagnosis
Salmonellosis is diagnosed through stool or blood tests. Differentiation from other gastroenteritis types is very important for accurate treatment.
Treatment
For mild cases, treatment involves oral rehydration and electrolyte replacement. Severe cases may require intravenous fluids. Antibiotics like ceftriaxone are reserved for high-risk patients or those with systemic infection. Azithromycin is preferred for treating resistant typhoid cases.
Epidemiology
United States
In the US, salmonellosis causes approximately 1.35 million illnesses, 26,500 hospitalizations, and 420 deaths annually. Despite efforts to control the infection, the rate has risen from 2001 to 2011.
Europe
Europe has experienced significant outbreaks, such as the 2012 Salmonella thompson outbreak linked to smoked salmon. Turkey production has also been identified as a source of infection.
Elsewhere
Global incidents include mass infections in Russia and Singapore due to contaminated food and widespread poultry contamination in South Africa and Egypt.
Immunological Response
From an immunological perspective, Salmonella infiltrates epithelial cells in the small intestine, inducing inflammation. The body's initial response involves neutrophils, monocytes, and dendritic cells. Protective immunity is primarily mediated by CD4+ T cells, with a significant role for Th1 and Th17 responses. B-cells are essential for resolving infections, acting independently of antibody secretion.
Research
Vaccine Development
Recent studies have focused on developing vaccines for both humans and chickens. A successful chicken vaccine has nearly eradicated salmonellosis in the UK.
Bacteriophage Treatment
Bacteriophage therapy offers an alternative treatment, targeting Salmonella specifically without affecting the intestinal microbiota. While promising, this method requires further research to ensure stability and efficacy.
Salmonellosis remains a significant public health challenge, necessitating ongoing research and improved preventive measures to control its spread and impact.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary manifestation of salmonellosis?
How long after infection do salmonellosis symptoms typically appear?
Which of the following is a symptom of typhoid fever caused by Salmonella?
What is a potential long-term effect of salmonellosis?
Which food handling practice is recommended by the FDA to prevent salmonellosis?
How is salmonellosis diagnosed?
What is the preferred antibiotic for treating resistant typhoid cases?
Approximately how many illnesses does salmonellosis cause annually in the United States?
Which cells are primarily involved in the protective immune response against Salmonella?
Which alternative treatment targets Salmonella specifically without affecting the intestinal microbiota?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


