Sarcoidosis
Overview
Sarcoidosis, also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease, is a systemic inflammatory condition characterised by the formation of granulomas—abnormal collections of inflammatory cells. It most commonly affects the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes, though any organ can be involved. The disease's cause is unknown, but genetic predisposition and environmental or infectious triggers are suspected.

Signs and Symptoms
Sarcoidosis symptoms vary depending on the organ affected:
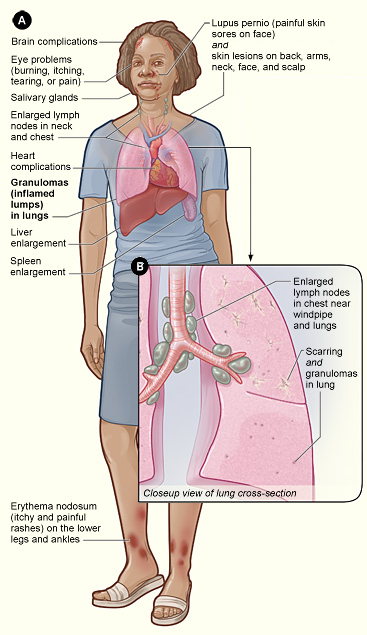
- Lungs: wheezing, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain.
- Skin: lumps, ulcers, discoloured skin, erythema nodosum.
- General: fatigue, weight loss, joint aches, arthritis.

Respiratory Tract
Lung involvement is most common, occurring in at least 90% of cases, and can lead to progressive fibrosis. The disease stages in the lungs are classified radiologically:
- Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (BHL) alone.
- BHL with pulmonary infiltrates.
- Pulmonary infiltrates without BHL.
- Fibrosis.
Cardiac
Cardiac sarcoidosis can cause arrhythmias, heart block, and heart failure. Autopsy studies reveal cardiac involvement in 20-30% of cases in the US and up to 60% in Japan.
Eyes
Eye involvement includes uveitis and retinal inflammation, potentially leading to loss of vision. Heerfordt syndrome involves anterior uveitis, parotitis, facial nerve paralysis, and fever.
Nervous System
Neurosarcoidosis affects the cranial nerves and can present with facial nerve palsy, optic nerve dysfunction, chronic meningitis, and peripheral neuropathy.
Endocrine and Exocrine
Sarcoidosis can lead to hypercalcaemia due to increased production of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D. Thyroid dysfunction and parotid gland enlargement are also observed.
Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary
Though rare, sarcoidosis can affect the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, mimicking Crohn's disease or leading to nephrocalcinosis.
Blood
Common blood anomalies include lymphopenia, anaemia, and monocytosis. Hypergammaglobulinaemia is also frequently observed.
Bone, Joints, and Muscles
Musculoskeletal involvement leads to acute or chronic arthritis, often associated with Löfgren syndrome.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made through exclusion, involving imaging and biopsy to rule out other conditions like tuberculosis and lymphoma. A chest X-ray or CT scan can reveal lymphadenopathy.

Treatment
Treatment varies greatly, with many requiring no systemic therapy. For symptomatic cases, NSAIDs are first-line treatments. Corticosteroids like prednisone are standard for more severe cases. Steroid-sparing agents such as methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolic acid are used to reduce corticosteroid side effects. Immunosuppressants, like cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine, and biologic agents targeting TNF, such as infliximab, are reserved for refractory cases.
Specific Organ Treatments
Ursodeoxycholic acid is used for liver involvement, and antimalarials like chloroquine are effective for cutaneous sarcoidosis and hypercalcaemia. Thalidomide and phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors have shown promise in clinical trials for resistant cases.
Prognosis
Prognosis varies; many cases remit spontaneously or with treatment, while others may progress to chronic disease or pulmonary fibrosis. Mortality rates are higher in certain populations, such as African Americans.

Epidemiology
Sarcoidosis affects young adults, with a higher incidence in women and certain ethnic groups, particularly African Americans and Northern Europeans. The disease is less common in South America, India, and Canada.
History
First described in 1877, sarcoidosis has been known by various names. Significant milestones include the identification of lung involvement in 1915 and the first international sarcoidosis conference in 1958.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is sarcoidosis primarily characterised by?
Which organ is most commonly affected by sarcoidosis?
What is the first radiological stage of lung involvement in sarcoidosis?
What percentage of sarcoidosis cases involve the lungs?
Which syndrome involves anterior uveitis, parotitis, facial nerve paralysis, and fever?
Which blood anomaly is commonly observed in sarcoidosis?
What is the first-line treatment for symptomatic sarcoidosis?
Which immunosuppressant is reserved for refractory cases of sarcoidosis?
Which demographic has a higher incidence of sarcoidosis?
In what year was the first international sarcoidosis conference held?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


