Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. It primarily affects the urinary tract or intestines, with symptoms including abdominal pain, diarrhoea, bloody stool, and blood in the urine. Prolonged infection may result in liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer. Children may experience poor growth and learning difficulties. The disease is spread through contact with freshwater contaminated by the parasites, which are released from infected snails.
Signs and Symptoms


Many individuals remain asymptomatic. Symptoms, if they appear, typically manifest 4–6 weeks post-infection. Initial symptoms may include general malaise, tingling, or a light rash known as "swimmer's itch." Acute schistosomiasis (Katayama fever) may occur weeks to months after infection, presenting symptoms like fever, muscle aches, and cough. Chronic infection can lead to more severe complications such as intestinal or urogenital schistosomiasis, hepatosplenic schistosomiasis, pulmonary schistosomiasis, and neuroschistosomiasis.
Diagnosis
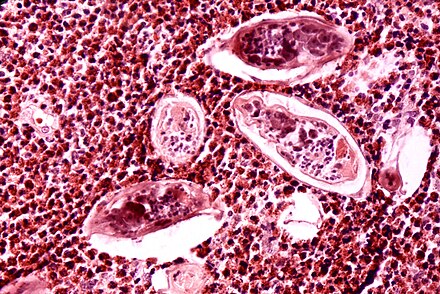

Diagnosis is primarily confirmed by identifying parasite eggs in stool or urine samples using microscopic examination. Antibody detection can be useful for individuals who have travelled to endemic areas but do not show eggs in their samples. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing is accurate but not widely used in low-resource settings due to cost. Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, and MRI can assess organ damage and severity of infection.
Transmission and Life Cycle


Schistosomiasis is transmitted when individuals come into contact with contaminated freshwater. The lifecycle involves multiple stages, including the release of eggs into water through faeces or urine, infection of freshwater snails, and release of infectious larvae (cercariae) that penetrate human skin.
Prevention

Preventive measures include improving access to clean water and sanitation, educating communities about hygiene, and using molluscicides to reduce snail populations. The World Health Organisation recommends preventive anthelminthic administration, treating entire populations in high-risk areas using praziquantel.
Treatment

The primary treatment for schistosomiasis is praziquantel, which is effective against adult schistosomes but not the eggs or immature worms. Repeated treatment may be necessary to ensure complete eradication. Oxamniquine is an alternative for S. mansoni infections. Treatment guidelines by the WHO recommend different strategies based on the prevalence of symptoms in a community.
Epidemiology

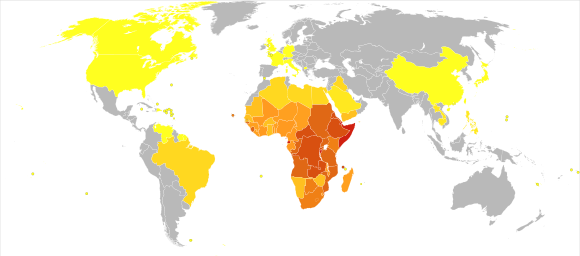
Schistosomiasis is prevalent in tropical regions, particularly in Africa, Asia, and South America. In 2019, it affected approximately 236.6 million people globally. The disease is a significant public health concern, second only to malaria among parasitic diseases in terms of socio-economic impact. Death estimates vary, with the WHO estimating up to 200,000 annual deaths related to schistosomiasis.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary cause of schistosomiasis?
Which symptom is NOT typically associated with schistosomiasis?
How is schistosomiasis primarily transmitted?
What is the initial symptom of schistosomiasis known as "swimmer's itch" caused by?
Which diagnostic method is primarily used to confirm schistosomiasis?
Which drug is commonly used to treat schistosomiasis?
What is the purpose of using molluscicides in schistosomiasis prevention?
What severe complication can result from prolonged schistosomiasis infection?
Which organisation recommends the use of preventive anthelminthic administration in high-risk areas for schistosomiasis?
In which regions is schistosomiasis most prevalent?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


