Sickle Cell Disease

Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of haemoglobin-related blood disorders typically inherited and marked by an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin. The most common type is sickle cell anaemia. The abnormal haemoglobin (HbS) leads to rigid, sickle-shaped red blood cells, causing various health problems starting around 5 to 6 months of age.
The average life expectancy in the developed world ranges from 40 to 60 years. All major organs can be affected due to the disease's impact on small blood vessels.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs of sickle cell disease usually begin in early childhood. Symptoms can vary in severity and frequency, with common early symptoms including pain and swelling in the hands and feet (dactylitis), pallor, jaundice, and fatigue due to anaemia. Acute and chronic complications include:
- Vaso-occlusive crisis: Painful episodes caused by sickle-shaped cells obstructing capillaries.
- Splenic sequestration crisis: Acute enlargement of the spleen due to trapped red cells.
- Acute chest syndrome: Characterised by chest pain, fever, and respiratory symptoms.
- Aplastic crisis: Triggered by parvovirus B19, leading to decreased red blood cell production.
- Haemolytic crisis: An accelerated drop in haemoglobin levels due to rapid red blood cell breakdown.

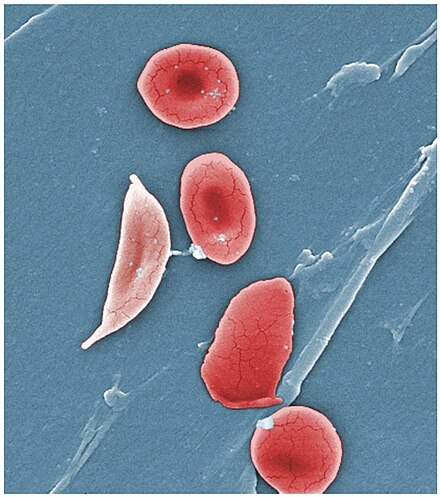
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through blood tests. In many countries, newborns are screened for SCD. Key diagnostic methods include:
- Complete blood count (CBC): Reveals haemoglobin levels and reticulocyte counts.
- Blood film: Shows sickling of red blood cells.
- Haemoglobin electrophoresis: Identifies abnormal haemoglobin forms.
- Genetic testing: Rarely performed but definitive.

Treatment
Management of sickle cell disease includes a variety of measures aimed at preventing complications and managing symptoms:
- Medications: Pain management with opioids, folic acid supplementation, and hydroxyurea to reduce the frequency of pain episodes.
- Blood transfusions: Used to treat severe anaemia and prevent stroke.
- Bone marrow transplant: The only known cure, though difficult to obtain due to specific HLA typing requirements.
Folic Acid and Penicillin
Penicillin is recommended from birth to five years of age to combat infections due to an immature immune system. Folic acid supplementation, previously recommended by WHO, shows unclear effects on anaemia symptoms.
Vaso-occlusive Crisis
Painful crises are treated with hydration, analgesics, and blood transfusions. Crizanlizumab, approved in 2019, reduces the frequency of vaso-occlusive crises.
Stroke Prevention
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound can detect children at high risk for stroke, and blood transfusions can reduce the risk. Hydroxyurea is recommended for children and adults with severe complications.
Acute Chest Syndrome
This condition is managed with antibiotics, oxygen supplementation, and blood transfusion if necessary.
Hydroxyurea
Hydroxyurea reduces the frequency of painful episodes and increases survival time by reactivating foetal haemoglobin production. Voxelotor, approved in 2019, increases haemoglobin levels in SS disease.
Gene Therapy
In 2023, gene therapies such as exagamglogene autotemcel and lovotibeglogene autotemcel were approved. CRISPR-Cas9 and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) are other emerging treatments.

Prognosis and Epidemiology
Approximately 90% of individuals survive to age 20, and close to 50% survive beyond age 50. The disease is most prevalent in tropical regions, especially sub-Saharan Africa, where about 80% of cases occur. Migration has increased prevalence in Europe and the United States, where around 100,000 people are affected.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which protein is abnormal in sickle cell disease?
At what age do symptoms of sickle cell disease typically start appearing?
Which of the following is NOT a common acute complication of sickle cell disease?
What is the primary method used to diagnose sickle cell disease in newborns?
Which medication is known to reduce the frequency of painful episodes in sickle cell disease?
What is the main cause of the painful vaso-occlusive crises in sickle cell disease?
Which organ is commonly affected by splenic sequestration crisis in sickle cell disease?
What is the primary goal of blood transfusions in managing sickle cell disease?
Which gene is responsible for sickle cell anaemia?
Which recent therapeutic development aims to treat sickle cell disease at the genetic level?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


