Sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses, leading to symptoms such as thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain.
It is commonly seen in individuals with underlying conditions such as allergies or structural nasal problems, and those with lower immunity. Most cases are caused by viral infections, but bacterial and fungal infections can also be culprits.

Signs and Symptoms
The primary symptoms of sinusitis include headache, facial pain, or pressure, particularly over the affected sinuses, which can worsen when bending over or lying down. Acute sinusitis may present with a thick, green nasal discharge possibly containing pus or blood. Localised headaches, toothaches, and postnasal drip are also common. Chronic sinusitis can lead to symptoms like nasal congestion, facial pain, night-time coughing, and an increased severity of asthma symptoms. Additionally, anosmia (loss of smell) is frequently observed in chronic cases.

Diagnosis
Sinusitis is classified into several categories based on duration and recurrence: acute (up to four weeks), subacute (4-12 weeks), chronic (over 12 weeks), and recurrent acute (four or more episodes per year). Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms, but imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs may be used for chronic cases or when complications are suspected.



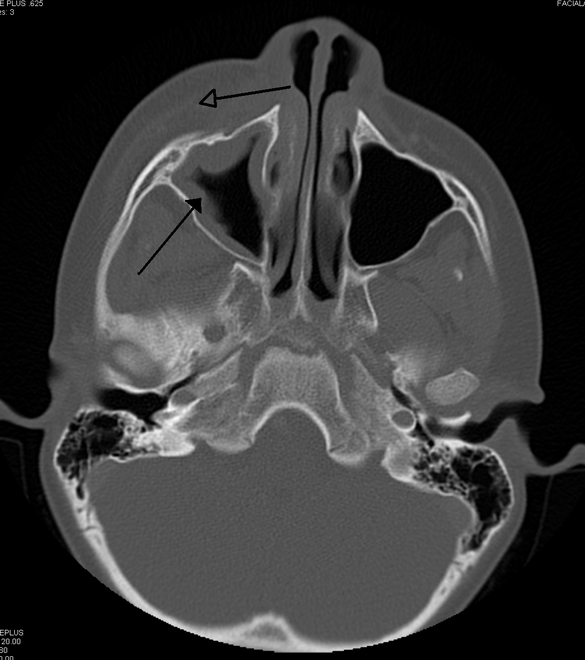


Treatment
Treatment for sinusitis varies depending on the cause and severity. For most cases, rest and hydration are recommended. Nasal irrigation can help relieve congestion, while decongestant nasal sprays may offer temporary relief. Antibiotics are generally reserved for bacterial sinusitis that does not improve within 10 days or worsens. Amoxicillin or amoxicillin/clavulanate is typically the first line of antibiotic treatment, with the latter being slightly more effective.


Nasal corticosteroids may be useful for reducing inflammation, particularly in chronic sinusitis. Surgery, such as Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) or balloon sinuplasty, may be considered for chronic or recurrent cases that do not respond to medical treatments.

Complications
Complications of sinusitis, although rare, can be severe. These include orbital cellulitis, brain abscesses, and meningitis. Early diagnosis and treatment are very important for preventing such outcomes. Chronic sinusitis may also lead to chronic mouth breathing, increasing the risk of gingivitis.
Epidemiology
Sinusitis is prevalent, affecting between 10% and 30% of people each year in the developed world. Chronic sinusitis affects about 12.5% of people, leading to significant healthcare costs. The condition is commonly mismanaged with unnecessary antibiotic treatments for viral infections, contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary cause of most sinusitis cases?
Which of the following is a common symptom of chronic sinusitis?
How long does acute sinusitis typically last?
Which imaging study is commonly used for diagnosing chronic sinusitis?
What is the first line of antibiotic treatment for bacterial sinusitis?
Which complication is NOT typically associated with sinusitis?
What percentage of people in the developed world are affected by sinusitis each year?
Which treatment is often reserved for chronic or recurrent sinusitis that does not respond to medical treatment?
Which symptom is frequently observed in chronic sinusitis cases?
Which of the following conditions is commonly mismanaged with unnecessary antibiotic treatments?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


