Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, which can be acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis usually has a rapid onset and is characterised by symptoms such as a sore throat, fever, enlarged tonsils, trouble swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes around the neck. Complications can include a peritonsillar abscess, also known as quinsy.
Causes
Tonsillitis is most commonly caused by viral infections, including adenovirus, rhinovirus, coronavirus, influenza virus, and Epstein-Barr virus, among others. Bacterial infections, particularly by Group A β-hemolytic streptococci (GABHS), can also cause tonsillitis, leading to strep throat. Less common bacterial causes include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The infection is typically spread through the air from person to person.

Signs and Symptoms
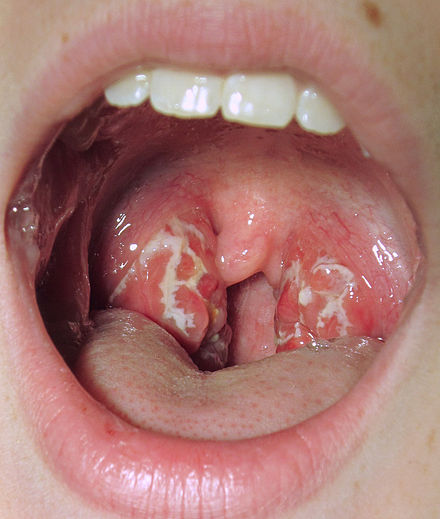
Individuals with tonsillitis generally experience a sore throat, painful swallowing, malaise, and fever. The tonsils and sometimes the back of the throat appear red and swollen, with possible white discharge. Swelling of the cervical lymph nodes is also common. Viral infections may also cause cough, runny nose, hoarseness, or blistering in the mouth or throat, while infectious mononucleosis can cause tonsillar swelling with red spots or white discharge, along with other systemic symptoms.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis may involve clinical assessment and laboratory tests. The Centor criteria are used to evaluate the likelihood of GABHS infection based on the presence of tonsillar exudate, painful neck lymph nodes, history of fever, age between five and fifteen years, and absence of cough. Confirmation can be achieved through throat swabs and rapid strep tests.

Treatment
Pain and Symptom Management
Treatment often involves managing pain and symptoms using paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, warm salt water gargles, lozenges, honey, or warm liquids. There are no specific antiviral treatments for virally caused tonsillitis.
Antibiotics
For bacterial tonsillitis caused by GABHS, antibiotics such as penicillin or amoxicillin are usually prescribed. Cephalosporins and macrolides can be used as alternatives for those allergic to penicillin. Antibiotic treatment typically lasts seven to ten days.
Pain Medication
Pain relief can be achieved using paracetamol and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Opioids like codeine are generally avoided in children under 12 years. Anaesthetic mouthwash can provide symptomatic relief.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are effective in reducing pain and improving symptoms within 24 to 48 hours. Oral corticosteroids are recommended unless the patient is unable to swallow medications.
Surgery
In cases of recurrent tonsillitis or significant obstruction, a tonsillectomy may be performed to remove the tonsils. This procedure has been found to be more effective and cost-efficient compared to medical treatment alone, especially in adults with frequent episodes.
Prognosis and Complications
Since the introduction of penicillin, the focus has been on preventing complications such as rheumatic fever, which can affect the nervous system and heart. Other complications include dehydration, kidney failure, blocked airways, and peritonsillar abscesses. Rarely, the infection can spread to the internal jugular vein, causing Lemierre's syndrome, or lead to post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Epidemiology
Tonsillitis is common worldwide, particularly in school-aged children, and typically occurs during colder months. Most children experience tonsillitis at least once, with bacterial infections more common at a later age.
Historical and Cultural Context
Tonsillitis has been documented since ancient times, including in the Greek Hippocratic Corpus. Recurrent tonsillitis can notably affect individuals who rely on their vocal abilities professionally.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of acute tonsillitis?
What is the most common bacterial cause of tonsillitis?
Which diagnostic criteria are used to evaluate the likelihood of GABHS infection in tonsillitis?
Which of the following is a complication of untreated bacterial tonsillitis?
What is typically used to confirm a diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis?
For pain relief in tonsillitis, which of the following is generally NOT recommended for children under 12 years?
Which of the following is NOT a common viral cause of tonsillitis?
When is a tonsillectomy typically considered for a patient with tonsillitis?
Which age group is most commonly affected by tonsillitis?
Which medication is commonly prescribed for bacterial tonsillitis caused by GABHS?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


