Tourette Syndrome
Tourette Syndrome (TS) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder manifesting in childhood or adolescence, characterised by multiple motor tics and at least one vocal tic. These tics include blinking, coughing, throat clearing, sniffing, and facial movements, often preceded by an unwanted urge or sensation known as a premonitory urge. TS is at the severe end of the spectrum of tic disorders and was once viewed as rare and bizarre, often linked with coprolalia (the utterance of obscene words), although this occurs in only a minority of cases.

Classification
TS is classified under neurodevelopmental disorders in the DSM-5 and as a disease of the nervous system in the ICD-11. Diagnosis requires multiple motor tics and at least one vocal tic for over a year, with onset before age 18. Tics are sudden, repetitive, nonrhythmic movements or sounds that are distinct from other movement disorders like choreas and dystonias.
Signs and Symptoms
Tics
Tics in TS wax and wane, changing in number, frequency, severity, and location. These can be motor tics, such as blinking and facial movements, or vocal tics like throat clearing. Complex tics can include actions like touching or repeating words (coprolalia, echolalia, palilalia). Tics often worsen with stress or fatigue and can be temporarily suppressed at the cost of mental exhaustion.
Onset and Progression
Typical onset is between five and seven years, peaking in severity at ages eight to twelve. Although symptoms usually decrease during adolescence, severe tics can persist into adulthood for a minority. Early tics often affect the head and shoulders, and vocal tics may appear later.
Co-occurring Conditions
TS often coexists with conditions like ADHD and OCD, which may cause more impairment than the tics themselves. Mood disorders, anxiety, and disruptive behaviours are also common. Co-occurring conditions require careful assessment as they significantly affect overall functioning.

Causes and Mechanism
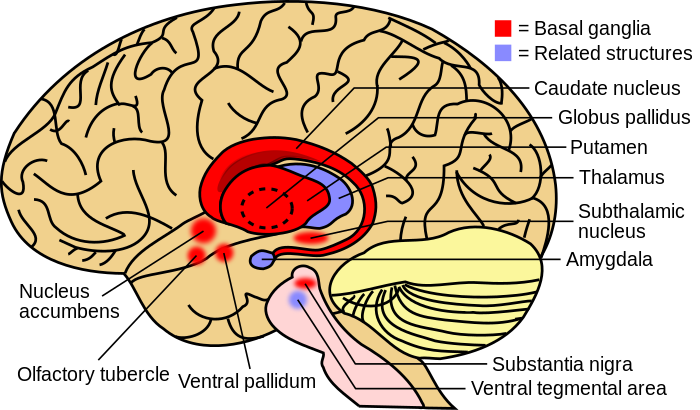
TS is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors, with evidence pointing to genetic heritability. Dysfunction in neural circuits, particularly involving the basal ganglia, thalamus, and frontal cortex, is implicated in the mechanism of TS. Imaging studies suggest abnormalities in cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuits and dysregulated dopaminergic transmission.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of TS is based on clinical observation of symptoms and family history, with the exclusion of other conditions that may cause tics. There are no specific tests for TS, making history and symptom observation very important. Diagnosis may be delayed due to misconceptions about the disorder.
Differential Diagnosis
Conditions that mimic TS, known as tourettism, must be ruled out. These include other movement disorders like choreas and dystonias, as well as developmental disorders such as autism. Functional tic-like movements, often linked to psychological factors, also need differentiation from organic tics.
Management
There is no cure for TS, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and comorbid conditions.
Psychoeducation and Social Support
Education for the patient, family, and community is very important. Understanding TS can alleviate anxiety and prevent unnecessary treatments. Supportive psychotherapy and school accommodations may help children affected by TS.
Behavioural Therapies
Habit reversal training (HRT) and comprehensive behavioural intervention for tics (CBIT) are first-line treatments. These therapies help individuals develop competing responses to tics.
Medication
Medications are reserved for severe symptoms and include neuroleptics like risperidone and aripiprazole, and antihypertensives like clonidine and guanfacine. Medications are used at the lowest effective dose to minimise adverse effects.

Other Treatments
Complementary and alternative medicine approaches lack proven benefits. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is experimental and reserved for severe, treatment-resistant cases.
Prognosis
TS symptoms often lessen with age, and individuals with TS have a normal life expectancy. Most children see a reduction in tics by adulthood, and the condition does not affect intelligence or life span. Supportive environments and coping strategies significantly influence quality of life.

Epidemiology
TS is more common than previously thought, affecting about 1% of children and adolescents. It is more prevalent in males and often goes undiagnosed in milder cases. Observed prevalence is higher among children due to the natural remission of tics with age.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the primary characteristic required for a diagnosis of Tourette Syndrome (TS)?
At what age does Tourette Syndrome typically onset?
Which of the following is not a common co-occurring condition with TS?
What is a premonitory urge in the context of TS?
Which brain structures are implicated in the mechanism of TS?
What is the role of habit reversal training (HRT) in managing TS?
Which medication is typically tried first when medication is needed for TS?
Which of the following is true about the prognosis of TS?
According to the text, what affects the quality of life for individuals with TS?
Which of the following is a common misconception about TS?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


