Varicocele
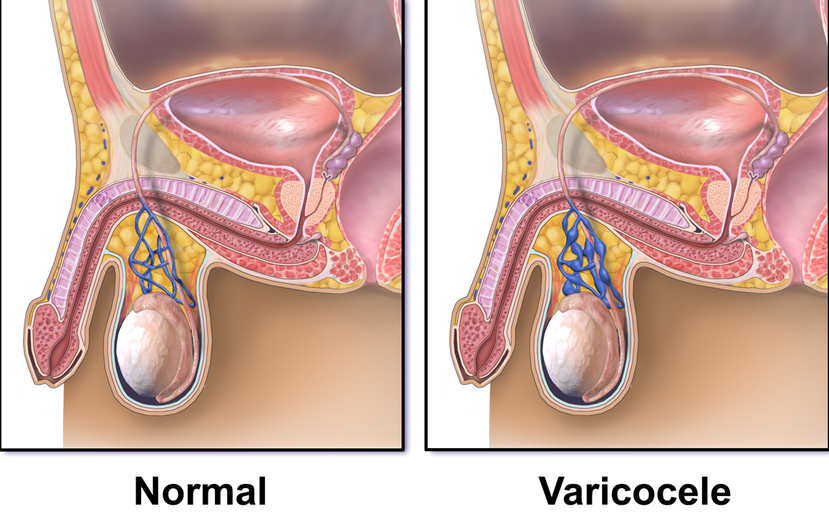
A varicocele is an abnormal enlargement of the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum, which is part of the spermatic cord that drains blood from the testicles back to the heart. In females, it presents as a painful swelling of the anatomically similar plexus and is often referred to as pelvic compression syndrome. Varicoceles are prevalent in about 15% to 20% of men, with the incidence increasing with age.

Overview
Signs and Symptoms
Varicocele usually manifests as soft lumps above the testicle, predominantly on the left side of the scrotum, although right-sided and bilateral varicoceles do occur. Men may experience pain or a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum. Large varicoceles can appear as a plexus of veins, often described as a "bag of worms". The condition is sometimes discovered during investigations for male infertility.
Cause

There are three primary theories explaining the anatomical cause of varicocele:
- The left-side vein connects to the larger outflowing vein at a right angle, which tends to fail.
- Testicular valves that prevent backflow fail, leading to the swelling and compression of the valveless pampiniform plexus.
- Excessive pressure in upstream veins, due to nutcracker syndrome, contributes to the condition.
Pathophysiology
The primary concern with varicocele is its potential effect on male fertility. The relationship between varicocele and infertility is not well understood. Some men with varicocele remain fertile, while others exhibit compromised sperm function or abnormal sperm morphology. Potential mechanisms affecting sperm function include damage from excess heat due to blood pooling and oxidative stress.
Factors such as tobacco smoking and genetic mutations in the gene expressing glutathione S-transferase Mu 1 can increase the risk of infertility and exacerbate varicocele's impact on fertility.
Diagnosis
Varicocele can be confirmed through scrotal ultrasound, which measures the dilation of the veins in the pampiniform plexus.

Criteria
Varicoceles are categorised into grades. The Dubin and Amelar classification divides varicoceles into three grades based on palpability:
- Grade 1: Palpable only during the Valsalva manoeuvre while standing.
- Grade 2: Palpable at rest while standing.
- Grade 3: Visible through the scrotal skin without additional manoeuvres.
The Sarteschi classification system further details five grades, from reflux occurring solely during the Valsalva manoeuvre without scrotal deformation (Grade I) to resting reflux with testicular atrophy (Grade V).
Imaging
Manual examination of the scrotum is essential for interpreting ultrasound images. During the ultrasound, vein diameters are measured, and regurgitation is assessed, particularly during the Valsalva manoeuvre.
Treatment

Surgical approaches to treat varicocele include retroperitoneal, infrainguinal/subinguinal, and inguinal methods, with percutaneous embolisation being another option. Potential complications of surgery include haematoma, hydrocele, infection, and injury to the scrotal tissue or structures, including the testicular artery, which may result in loss of a testicle.
Prognosis
The effectiveness of varicocele surgery or embolisation in improving male fertility is controversial. While some evidence suggests that varicocelectomy may improve fertility in men with abnormal sperm, the number needed to treat is relatively high. A 2012 Cochrane review (updated in 2021) found tentative but unclear evidence of improved fertility post-treatment. The efficacy of sclerotherapy remains uncertain.
Epidemiology
Varicocele affects around 15% to 20% of adult males, up to 35% to 40% of men evaluated for infertility, and approximately 80% of men infertile due to other causes.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is a varicocele?
Which side of the scrotum is most commonly affected by varicocele?
What symptom is often associated with varicocele?
Which of the following theories is NOT one of the primary explanations for the cause of varicocele?
What is the relationship between varicocele and male fertility?
What diagnostic tool is commonly used to confirm varicocele?
According to the Dubin and Amelar classification, what is a Grade 1 varicocele?
What is a potential complication of varicocele surgery?
What is the general prognosis for varicocele surgery in improving fertility?
Which population has the highest prevalence of varicocele?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


