Warts
Introduction
Warts, medically known as verrucae or papillomas, are small, rough growths on the skin that can resemble a cauliflower or a solid blister. These are non-cancerous viral growths typically found on the hands and feet but can also occur on the genitals or face.
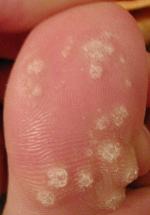
Signs & Symptoms
Warts present as skin growths and are most commonly found on the hands, feet, or genitals. They can appear singly or in multiples and vary in appearance based on their type. General symptoms include roughened surfaces, flesh-coloured, flat growths, or thread-like projections. They can be painful, especially when located on pressure points such as the soles of the feet.
Types of Warts
A range of wart types exist, each varying in shape, location, and the specific human papillomavirus (HPV) involved:

- Common wart (verruca vulgaris): Raised with a roughened surface, typically on hands.
- Flat wart (verruca plana): Small, smooth, and flesh-coloured.
- Filiform wart: Thread-like projections, often on the face.
- Genital wart (condyloma acuminatum): Occurs on genitalia, sexually transmitted.
- Periungual wart: Cauliflower-like, around the nails.
- Plantar wart (verruca plantaris): Hard, painful, usually on the soles of the feet.
- Mosaic wart: Clusters of plantar-type warts.
Cause
Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), of which there are about 130 known types. Each HPV type can infect specific areas of the body, causing benign growths or warts. Common warts are typically caused by HPV types 2 and 4, while genital warts are usually associated with types 6 and 11.
Pathophysiology
Under a microscope, warts show thickening of the stratum corneum (hyperkeratosis), stratum spinosum (acanthosis), and stratum granulosum. There are also large blood vessels at the dermoepidermal junction.

Diagnosis
Dermatoscopic examination often reveals fingerlike or knoblike extensions. Biopsy and histopathological examination can confirm the diagnosis.
Prevention
Vaccines like Gardasil 6 and Gardasil 9 are effective in preventing infections by HPV types responsible for cervical cancers and genital warts. However, these vaccines do not cover strains responsible for plantar warts. Preventive measures include avoiding direct contact with warts, not walking barefoot in public areas, and practising safe sex.
Treatment
Medication
- Salicylic acid: Effective in concentrations higher than over-the-counter products.
- Fluorouracil: A chemotherapy agent used for resistant warts.
- Imiquimod: Topical cream for genital warts, enhancing immune response.
- Cantharidin: Causes blistering, used with podophyllin.
- Bleomycin: Chemotherapy drug injected into deep warts.
- Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB): Induces an allergic response.
- Cidofovir: Experimental antiviral treatment.
- Verrutop: Topical solution causing mummification of wart tissue.
- Silver nitrate: Available as a caustic pencil.
- Trichloroacetic acid: Used if other treatments fail.


Procedures

- Keratolysis: Removal of dead surface skin cells.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen.
- Electrodesiccation: Drying the wart with electric current.
- Laser treatment: Using pulse dye or CO2 lasers.
- Microwave treatment: Heating the wart tissue.
- Intralesional immunotherapy: Injection of immune system stimulants.
- Duct tape occlusion therapy: Applying duct tape over the wart.

Alternative Medicine
Traditional treatments include the application of Chelidonium majus latex. Folk remedies, such as using potato or water from a specific well, have been recorded.

History
Warts have been documented since the time of Hippocrates. The term verruca was first used by Daniel Sennert in 1636. The viral cause was proven by Giuseppe Ciuffo in 1907, and HPV was identified as the causative agent by Harald zur Hausen in 1976, leading to the development of HPV vaccines.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the medical term for warts?
Which HPV types are most commonly associated with common warts?
Which of the following is NOT a type of wart?
What vaccine is effective in preventing infections by HPV types responsible for cervical cancers and genital warts?
Which treatment involves the freezing of warts using liquid nitrogen?
What is the main cause of warts?
Which of the following is a chemotherapy agent used for resistant warts?
What characteristic features are revealed through dermatoscopic examination of warts?
Which type of wart is characterised by thread-like projections and often found on the face?
Who identified HPV as the causative agent of warts, leading to the development of HPV vaccines?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


