Whooping Cough
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious bacterial disease caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. It is characterised by severe coughing fits followed by a high-pitched whoop sound or gasp as the person breathes in.
The disease is vaccine-preventable, but symptoms can still occur in vaccinated individuals, typically in a milder form.
Overview
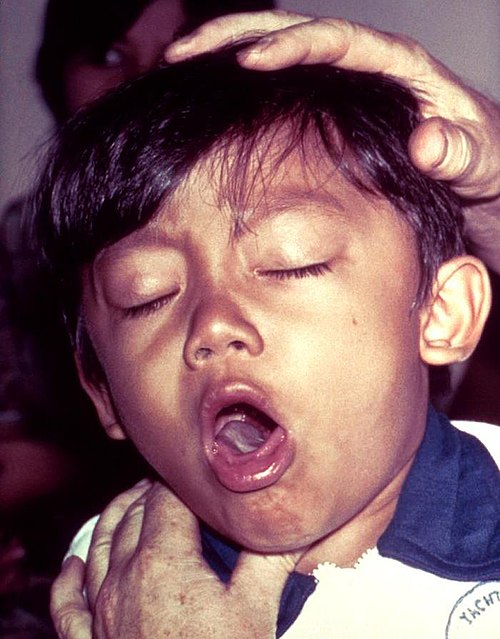
The disease starts with mild respiratory symptoms such as a runny nose, mild cough, and sneezing, known as the catarrhal stage. After one to two weeks, the classic symptom of uncontrollable coughing fits begins, often followed by a "whoop" sound. This paroxysmal stage can last between two to ten weeks or longer. During this stage, complications such as vomiting, rib fractures, and exhaustion may occur due to the violent nature of the cough. Following this is the convalescent stage, lasting one to four weeks, where the severity of the coughing fits gradually decreases.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically based on a combination of clinical symptoms and laboratory tests. A nasopharyngeal swab is commonly used for culturing the bacteria or for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing. Serological tests may be used in adults and adolescents to detect high levels of antibodies against pertussis toxin in the blood.
Cause and Mechanism
Pertussis is caused by Bordetella pertussis, an airborne bacterium spread through the coughs and sneezes of infected individuals. The bacteria adhere to the ciliated epithelium in the nasopharynx and multiply, secreting several toxins, including tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) and pertussis toxin, which contribute to the characteristic symptoms and complications of the disease. The toxins can lead to the destruction of ciliated cells, inhibition of mucus clearance, and pulmonary hypertension, which can be fatal in severe cases, particularly in infants.
Prevention
Vaccination is the primary method of preventing pertussis. The pertussis vaccine is recommended for routine immunisation by health organisations worldwide. The multicomponent acellular pertussis vaccine is generally 71-85% effective. However, immunity wanes over time, necessitating booster doses for older children and adults. Vaccination during pregnancy is highly effective in protecting infants during their early months of life.

Treatment
The primary treatment for pertussis is antibiotics such as erythromycin, clarithromycin, or azithromycin. These are most effective when started early, within three weeks of symptom onset. For infants and pregnant women, antibiotics are recommended within six weeks of symptom onset. While antibiotics can shorten the duration of infectiousness, they do not significantly alter the course of the disease if started late. Over-the-counter cough medications are not effective and are generally discouraged.
Prognosis
Most healthy older children and adults recover fully from pertussis, but the disease can be severe and sometimes fatal in newborns. Complications in infants under one year can include apnoea, pneumonia, seizures, and encephalopathy, often due to the bacterium's ability to suppress the immune system.
Epidemiology
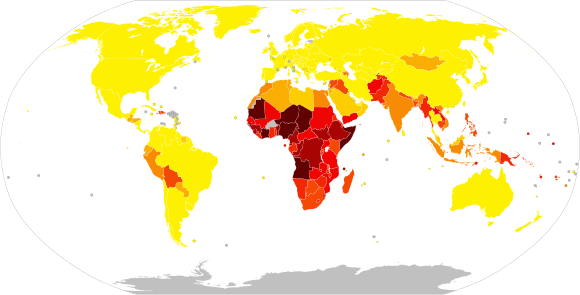
Pertussis is endemic worldwide, with more than 151,000 cases reported globally in 2018. Before the introduction of vaccines in the 1940s, the disease was a major cause of childhood morbidity and mortality. While vaccination has dramatically reduced incidence rates, pertussis remains a significant public health concern, particularly in developing countries. Cyclical epidemics occur every three to five years, and waning immunity and bacterial mutations pose ongoing challenges to disease control.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the causative agent of whooping cough?
Which stage of whooping cough is characterised by severe coughing fits followed by a "whoop" sound?
Which laboratory test is commonly used for diagnosing pertussis?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom during the catarrhal stage of whooping cough?
What is the primary method of preventing whooping cough?
Which antibiotic is NOT typically used for treating pertussis?
What is the main reason for administering the pertussis vaccine during pregnancy?
Which of the following complications is NOT commonly associated with pertussis in infants?
What is the primary mode of transmission for _Bordetella pertussis_?
Which stage of whooping cough involves a gradual decrease in the severity of coughing fits?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


