Wilson's Disease
Wilson's disease, also known as hepatolenticular degeneration, is a genetic disorder characterised by excessive copper accumulation in the body, primarily affecting the liver and brain.
The condition is autosomal recessive and results from mutations in the ATP7B gene, which is responsible for transporting excess copper into bile for excretion. Symptoms typically present between ages 5 and 35.

Signs and Symptoms
Liver Disease
Liver-related symptoms include jaundice, tiredness, increased bleeding tendency, and confusion due to hepatic encephalopathy. Portal hypertension can lead to oesophageal varices, splenomegaly, and ascites. Chronic active hepatitis often progresses to cirrhosis, although the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma remains low. In severe cases, patients may develop fulminant acute liver failure accompanied by haemolytic anaemia, leading to hepatic encephalopathy and brain swelling.
Neuropsychiatric Symptoms

Approximately half of the patients experience neurological or psychiatric symptoms. Initial signs include cognitive deterioration, clumsiness, and behavioural changes. Parkinsonism, characterised by cogwheel rigidity, bradykinesia, masked facial expressions, and tremors, is common. Patients may also exhibit ataxia, dystonia, seizures, and migraines.
Cognitive impairments can manifest as frontal lobe disorder or subcortical dementia, affecting memory and executive function. Psychiatric issues such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis often accompany neurological symptoms.
Other Organ Systems
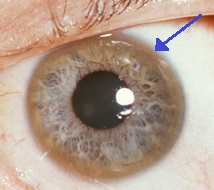
Wilson's disease can affect other organs, including the eyes, kidneys, heart, and musculoskeletal system. Kayser–Fleischer rings, caused by copper deposits in the cornea, are a hallmark of the disease. Renal tubular acidosis, cardiomyopathy, hypoparathyroidism, and osteoporosis are also associated with Wilson's disease.



Diagnosis

Diagnosis is challenging and often involves a combination of tests. Blood tests may reveal low ceruloplasmin levels and abnormal liver function. Elevated urine copper levels are indicative, and a 24-hour urine collection can confirm the diagnosis. Slit-lamp examination can detect Kayser–Fleischer rings.
A liver biopsy, measuring copper content and assessing liver damage, is the most accurate diagnostic method. Genetic testing for ATP7B mutations can confirm the diagnosis and aid in family screening.

Treatment
Diet
A low-copper diet is recommended, avoiding foods such as mushrooms, nuts, chocolate, dried fruit, liver, sesame seeds, sesame oil, and shellfish.
Medication
First-line treatment typically involves chelating agents like penicillamine or trientine, which bind copper and promote its excretion. Zinc supplements may be used to maintain stable copper levels once initial treatment is effective. Experimental treatments, such as tetrathiomolybdate, are under investigation. In rare cases, dimercaprol injections are necessary for severe neurological symptoms.
Physical and Occupational Therapies
Physiotherapy and occupational therapy can help manage neurological symptoms and prevent complications like contractures.
Transplantation
Liver transplantation is considered for patients with fulminant liver failure or advanced chronic liver disease unresponsive to medical treatment.
Genetics

Wilson's disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, requiring two copies of the mutated ATP7B gene. Approximately 300 mutations of ATP7B have been identified, with specific mutations prevalent in different populations.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What gene mutation is responsible for Wilson's disease?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT commonly associated with Wilson's disease?
What is a characteristic eye finding in Wilson's disease?
Which of the following is NOT a first-line treatment for Wilson's disease?
At what age do symptoms of Wilson's disease typically present?
Which organ system is primarily affected by Wilson's disease?
Which diagnostic method is considered the most accurate for Wilson's disease?
What pattern of inheritance does Wilson's disease follow?
Which dietary component should be avoided in Wilson's disease management?
Which part of the brain is primarily affected by Wilson's disease?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


