Zika Fever
Zika fever, also known as Zika virus disease, is an infectious disease caused by the Zika virus. The virus is primarily spread through the bite of infected mosquitoes of the Aedes genus, particularly Aedes aegypti. It can also be sexually transmitted and potentially spread via blood transfusions. The disease was first isolated in Africa in 1947 and later identified in humans in Nigeria in 1954.
Signs and Symptoms
Most individuals infected with Zika virus exhibit no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they are usually mild and include fever, rash, conjunctivitis (red eyes), muscle and joint pain, and headache. These symptoms typically last for several days to a week. Zika fever is often so mild that hospitalisation is seldom necessary. However, Zika virus infections have been strongly associated with Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS), a rapid onset of muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system, which can progress to paralysis.
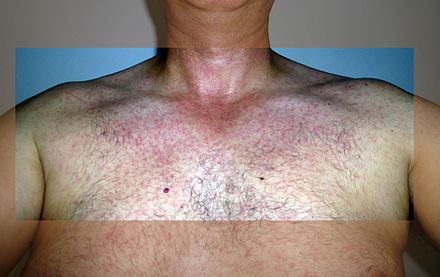
Guillain–Barré Syndrome
Zika virus infections can trigger Guillain–Barré syndrome, though it is difficult to definitively identify the virus as the cause. Several countries have reported increases in GBS cases during Zika outbreaks.
Pregnancy and Birth Defects
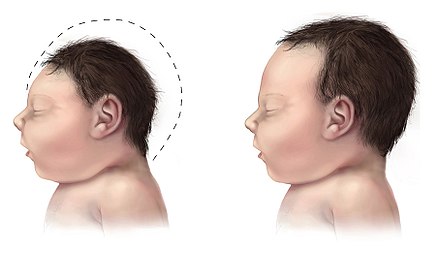
Zika virus can be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy, leading to severe birth defects such as microcephaly, where a baby's head is significantly smaller than expected. Other brain malformations and systemic abnormalities can also occur, leading to intellectual problems, seizures, and developmental delays.
Cause and Transmission
Zika virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus closely related to the dengue and yellow fever viruses. Transmission occurs mainly through mosquito bites but can also occur through sexual transmission, blood transfusions, and from mother to child during pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Zika fever is challenging due to symptom overlap with other illnesses such as dengue and chikungunya. Laboratory tests include reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) to detect viral RNA and serological tests for specific IgM and IgG antibodies. The World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends RT-PCR testing on serum collected within 1 to 3 days of symptom onset or on saliva and urine samples collected up to 14 days after symptom onset.
Prevention
Preventing Zika virus infection involves avoiding mosquito bites and practising safe sex. The use of insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus, wearing long-sleeved clothing, and using bed nets can reduce mosquito exposure. Eliminating standing water and using insecticides are also effective mosquito control measures. The CDC recommends that men who have travelled to Zika-affected areas use condoms or abstain from sex for six months to prevent sexual transmission.
CDC Travel Alert and WHO Response
In response to the Zika outbreak, the CDC issued travel alerts advising pregnant women to avoid areas with active Zika transmission. The WHO declared the Zika outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in February 2016, which was lifted in November 2016.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for Zika virus infection. Care is supportive, focusing on relieving symptoms such as pain, fever, and itching. Aspirin and NSAIDs are generally avoided due to the risk of hemorrhagic syndrome and Reye syndrome in children.
Epidemiology
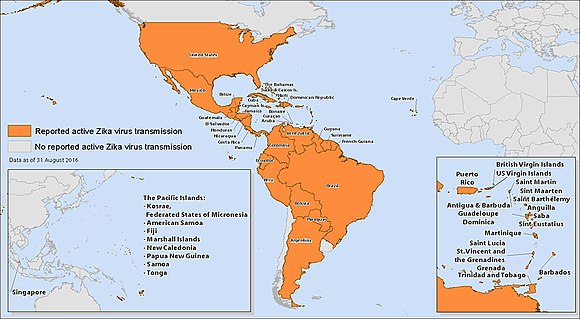
The Zika virus was first isolated in a rhesus monkey in the Zika Forest of Uganda in 1947. The first major human outbreak occurred in 2007 in the Yap Islands, followed by several outbreaks in the Pacific and the Americas. The 2015 outbreak in Brazil led to a surge in cases of microcephaly and prompted extensive public health measures.
Research
Research into Zika virus focuses on understanding its mechanism, developing vaccines, and controlling mosquito populations. Experimental methods include genetic modification of mosquitoes and infection with the Wolbachia bacterium to inhibit virus transmission.

Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Zika fever is primarily spread through the bite of infected mosquitoes of which genus?
What year was the Zika virus first isolated in humans?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of Zika fever?
Zika virus infections have been strongly associated with which neurological condition?
Zika virus can cause severe birth defects such as:
Which method is NOT a primary way to prevent Zika virus infection?
What type of diagnostic test does WHO recommend for detecting Zika virus within 1 to 3 days of symptom onset?
When did WHO declare the Zika outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern?
Which of the following is NOT a recommended treatment for Zika fever symptoms?
Which country experienced a major Zika outbreak in 2015 that led to a surge in cases of microcephaly?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


