Periodontal Disease: Pathology
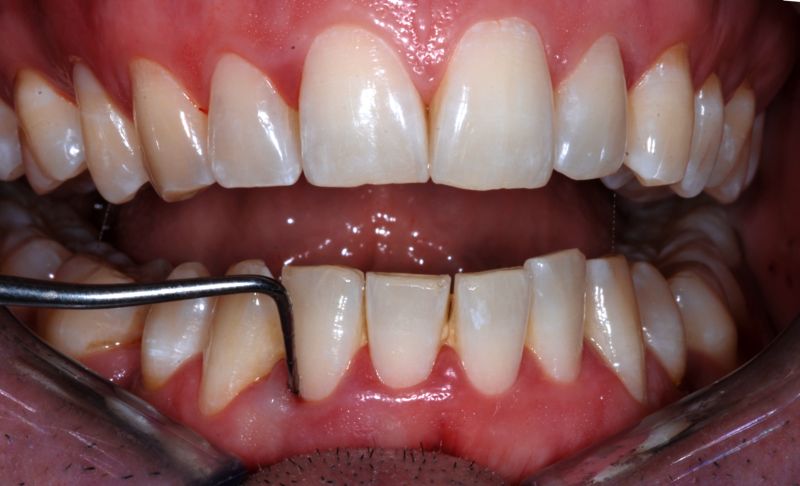
Periodontal diseases are among the most common conditions in dental practice, arising from complex interactions between bacterial toxins and the immune system. These conditions range from reversible gingivitis to irreversible periodontitis, where tissue destruction and alveolar bone loss occur.
This course explores the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases in detail, focusing on bacterial mechanisms, immune responses, and histological progression. Participants will gain insights into the role of bacterial toxins, the histological stages of disease progression, and the contributions of innate and adaptive immunity. This knowledge is essential for effective diagnosis, management, and treatment planning.
The course covers:
- The role of bacterial endotoxins and exotoxins in initiating and sustaining periodontal disease.
- Histological stages of periodontal disease progression.
- The interplay of innate and adaptive immune responses, including the roles of neutrophils, mast cells, T cells, and B cells.
- The impact of cytokines like IL-1 and TNF-alpha on alveolar bone loss.
Dental teams will also learn to integrate this knowledge into their practice, enhancing their ability to identify and manage periodontal diseases effectively.
Aim
The aim of the learning and teaching materials in this Dentaljuce module is to allow learners to develop their professional knowledge, understanding, and competence in the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases, enhancing their ability to diagnose, manage, and treat these conditions effectively in clinical practice.
Course objective
- To update members of the dental team with the latest insights into the role of bacterial toxins and immune responses in the progression of periodontal diseases.
Anticipated learning outcomes:
- Identify key bacterial toxins involved in periodontal disease and their mechanisms of action.
- Distinguish between the histological stages of periodontal disease progression and understand their clinical significance.
- Explain the role of neutrophils, mast cells, and dendritic cells in the innate immune response to periodontal pathogens.
- Analyze the function of T cells and B cells in adaptive immunity and their impact on periodontal health.
- Evaluate the role of cytokines, such as IL-1 and TNF-alpha, in alveolar bone loss and tissue destruction.
GDC Development Outcomes
This CPD will support the learner in meeting the following GDC Development Outcome(s): C.

