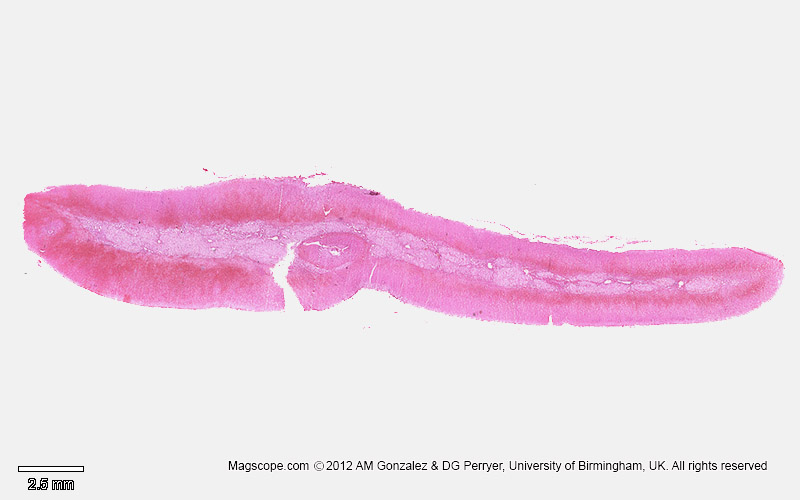
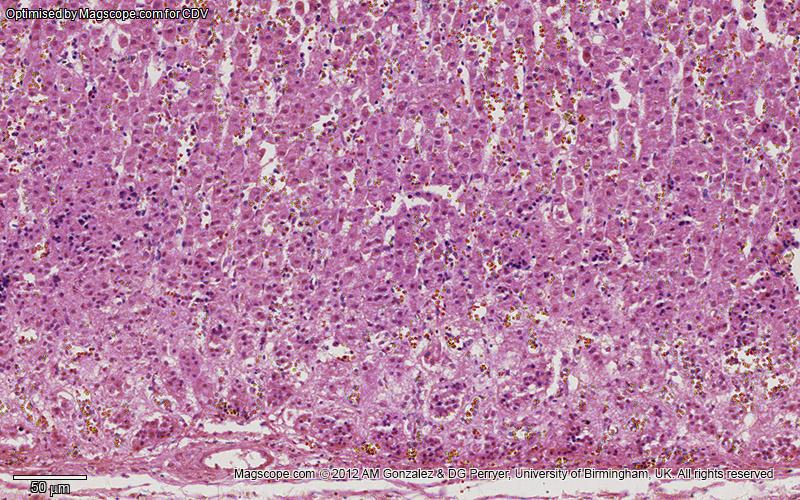
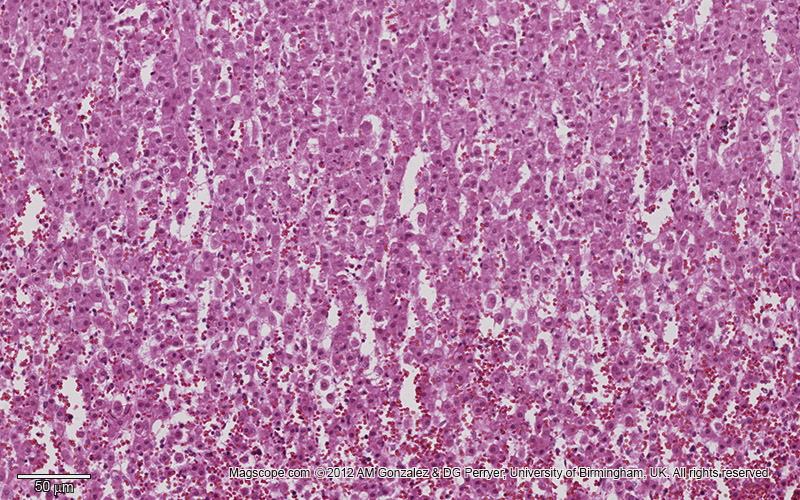
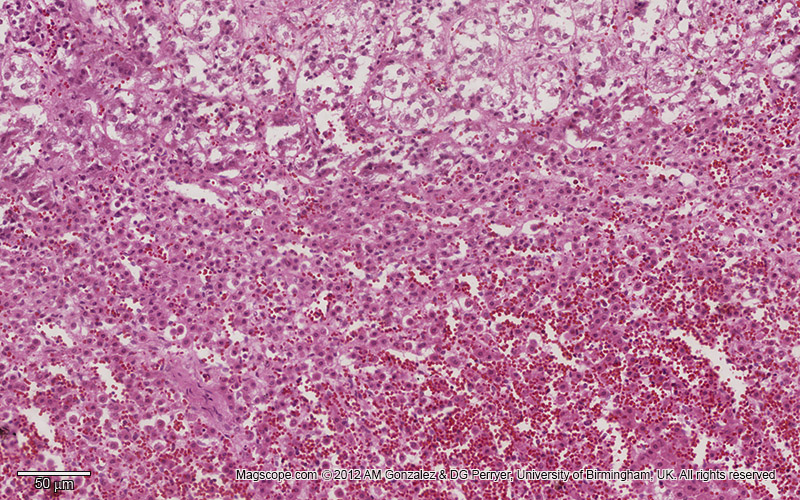
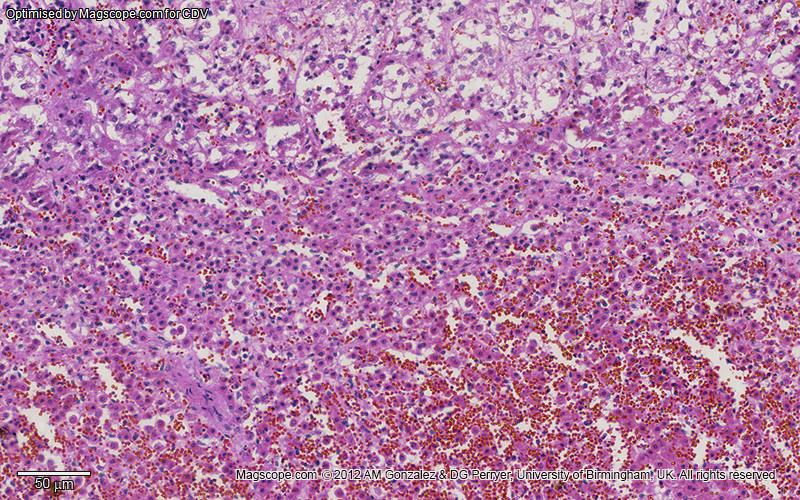
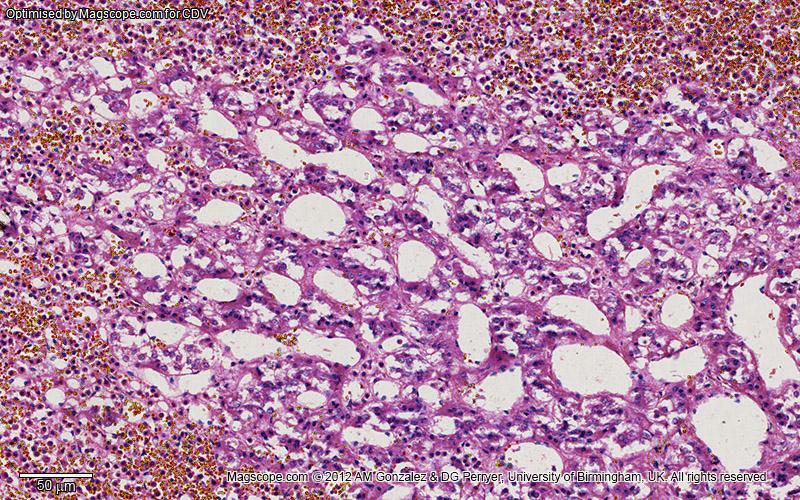
Histology
Adrenal gland
Many of the slides below are optimised for colour-blind people - click the spectrum icon.
Click here to scroll down to the accompanying text and MCQs.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
Which layer of the adrenal cortex is responsible for producing mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone?
What is the primary hormone produced by the adrenal medulla?
Histologically, the cells of the zona fasciculata are characterised by:
Addison's disease is characterised by destruction of which part of the adrenal gland?
Which artery does NOT supply blood to the adrenal glands?
Which of the following is a feature of primary aldosteronism?
Chromaffin cells are primarily found in which part of the adrenal gland?
What is a common cause of Cushing's syndrome?
Which venous structure drains the right adrenal gland?
Which feature is commonly observed in adrenal carcinoma histopathology?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!